L’artrite reumatoide (AR) è caratterizzata da infiammazione cronica, che porta a dolore articolare, rigidità e progressiva erosione delle articolazioni. I trattamenti tradizionali si concentrano principalmente sulla gestione dei sintomi e sul rallentamento della progressione della malattia. Tuttavia, spesso non riescono a fornire una cura definitiva o a far regredire i danni già presenti.
La terapia con cellule staminali per l’artrite reumatoide (AR) rappresenta un approccio all’avanguardia per il trattamento di questa malattia. Questo metodo sfrutta i meccanismi di rigenerazione del nostro corpo utilizzando cellule staminali — cellule indifferenziate in grado di trasformarsi in diversi tipi cellulari, inclusi quelli necessari per riparare i tessuti danneggiati.
Tra i vari tipi di cellule staminali, le cellule staminali mesenchimali (MSC) si dimostrano le più efficaci per il trattamento dell’AR. Queste cellule, che possono essere prelevate dal tessuto adiposo, dal midollo osseo o dal sangue del paziente, possiedono proprietà antinfiammatorie e immunomodulanti uniche. Modificando la risposta immunitaria e promuovendo la rigenerazione dei tessuti danneggiati, le MSC offrono un approccio a doppia azione per il trattamento dell’AR.
In questo articolo faremo una panoramica sull’artrite reumatoide, esaminando le prospettive della terapia con cellule staminali per il suo trattamento, e risponderemo a domande come: le cellule staminali possono essere utilizzate per trattare l’AR? Si può curare l’artrite reumatoide con le cellule staminali? Quali sono i benefici delle cellule staminali per l’AR? E molto altro ancora.
Cos’è l’artrite reumatoide?
L’artrite reumatoide (AR) è un disturbo autoimmune che colpisce principalmente le articolazioni. Può causare infiammazione cronica, dolore, rigidità e, infine, erosione delle articolazioni.
A differenza dell’osteoartrite, che deriva dall’usura fisica, l’AR si verifica quando il sistema immunitario attacca erroneamente i tessuti del corpo, in particolare la sinovia — la membrana che circonda le articolazioni.
Questa risposta immunitaria anomala provoca un’infiammazione che può ispessire la sinovia, danneggiando nel tempo la cartilagine e le ossa all’interno dell’articolazione.
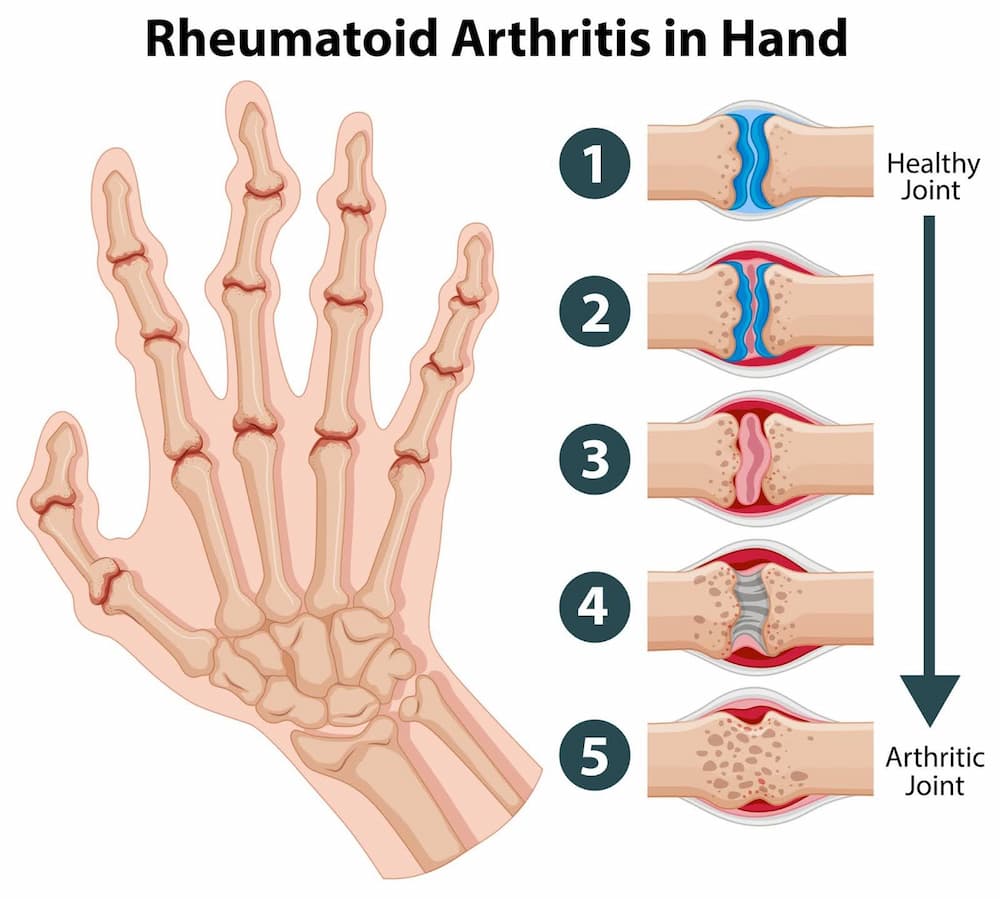
I sintomi dell’AR possono variare in gravità e sono temporanei, causando spesso disagio significativo e disabilità. La condizione può anche avere effetti sistemici, come l’affaticamento e il potenziale coinvolgimento di altri organi. Questo evidenzia la necessità di strategie terapeutiche efficaci per gestire questa complessa malattia.
Ottieni una consulenza online gratuita
Contattaci per conoscere i risultati attesi del trattamento, il suo costo e la sua durata.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
La terapia con cellule staminali funziona per l’artrite reumatoide?
Nella maggior parte dei casi, la terapia con cellule staminali è efficace per l’artrite reumatoide (AR), in quanto riduce potenzialmente l’infiammazione, promuove la riparazione dei tessuti e offre sollievo dal dolore. Tuttavia, l’efficacia della terapia con cellule staminali può variare significativamente tra gli individui e dipende da fattori come la gravità della malattia, lo stato generale di salute e i protocolli di trattamento specifici.
L’applicazione della cura dell’artrite reumatoide con le cellule staminali è diventata un punto focale della ricerca medica moderna, offrendo una speranza ai pazienti che cercano alternative ai trattamenti tradizionali per l’AR. La domanda che spesso ci si pone è: per l’artrite reumatoide giovanile curare con le cellule staminali potrebbe essere efficace? L’ARG attualmente non ha una cura definitiva, ma alcuni trattamenti, incluse le terapie con cellule staminali, sono in fase di studio per valutarne l’efficacia.
Questo approccio sfrutta le capacità rigenerative del corpo, con particolare attenzione alle cellule staminali mesenchimali (MSC) grazie alla loro capacità di differenziarsi in vari tipi cellulari, fornire effetti immunomodulanti e supportare la riparazione dei tessuti.
Indicazioni e controindicazioni per la terapia cellulare nell’artrite reumatoide
Le indicazioni per la terapia con cellule staminali includono, ma non si limitano a, gravi danni articolari, una risposta inadeguata ai trattamenti convenzionali e l’interesse per opzioni di terapia rigenerativa. Come accennato, per l’artrite reumatoide giovanile curare con le cellule staminali una delle soluzioni più promettenti, ma le controindicazioni possono includere infezioni attive, cancro o determinate condizioni mediche.
Indicazioni per la terapia con cellule staminali per l’artrite reumatoide
- Grave danno articolare
- Risposta inadeguata ai trattamenti standard
- Interesse per trattamenti rigenerativi
- Stadio precoce della malattia
- Dolore e infiammazione cronica
Controindicazioni per la terapia con cellule staminali per l’artrite reumatoide
- Pazienti con infezioni attive
- Persone con una storia di cancro negli ultimi 5 anni
- Diabete non controllato o malattie cardiovascolari
- Gravi disturbi di immunodeficienza
Vantaggi delle cellule staminali per curare l’artrite reumatoide
Curare l’artrite reumatoide con le cellule staminali offre promettenti vantaggi, tra cui la riduzione dell’infiammazione e il sollievo dal dolore. Inoltre, essa:
- Promuove la riparazione del tessuto articolare danneggiato e migliora la funzione articolare.
- Le cellule staminali mesenchimali hanno proprietà antinfiammatorie. Il ruolo delle cellule staminali mesenchimali nell’artrite reumatoide è, dunque, quello di contribuire a ridurre l’infiammazione cronica associata all’artrite reumatoide, portando potenzialmente a una riduzione del dolore e del gonfiore.
- Il trattamento risulta meno invasivo, con iniezioni che comportano un rischio inferiore di complicazioni e tempi di recupero più brevi.
- Le cellule staminali possono modulare la risposta del sistema immunitario, il che è utile nelle malattie autoimmuni come l’AR.
- La terapia con cellule staminali offre un approccio personalizzato alla gestione dell’artrite reumatoide.
- Rallenta la progressione dell’AR, offrendo benefici a lungo termine oltre la gestione dei sintomi.
Sicurezza della terapia con cellule staminali e possibili effetti collaterali
Le cellule staminali per la cura dell’artrite reumatoide, in particolare quando si utilizzano le cellule del paziente stesso (trapianto autologo), sono considerate generalmente sicure, con un rischio minore di rigetto immunitario e complicazioni.
Tuttavia, alcuni possibili effetti collaterali della terapia con cellule staminali includono:
- Come in ogni procedura che comporta iniezioni, c’è il rischio di infezione nel sito di iniezione, anche se è relativamente raro quando eseguito in un ambiente sterile.
- Sebbene meno comune con cellule staminali autologhe (prelevate dal paziente stesso), esiste comunque un leggero rischio di reazione immunitaria, soprattutto in caso di terapia con cellule staminali allogeniche (da donatore).
- Possono comparire gonfiore, dolore o rossore temporanei nel sito di iniezione, che solitamente scompaiono entro pochi giorni.
- Come in molte procedure mediche, esiste un piccolo rischio di sviluppare coaguli di sangue, soprattutto se ci sono condizioni preesistenti che promuovono la coagulazione.
- Potrebbe verificarsi una crescita di tessuti indesiderati. Esiste un rischio teorico che le cellule staminali possano differenziarsi in tipi di tessuti indesiderati o proliferare in modo incontrollato, anche se questo è estremamente raro con le attuali terapie mirate e controllate.
Prima di procedere con la terapia con cellule staminali, è necessario sottoporsi a una valutazione medica approfondita e discutere i potenziali rischi ed effetti collaterali con i professionisti sanitari. Il profilo di sicurezza della terapia con cellule staminali continua a migliorare grazie ai progressi nella ricerca medica e nelle tecnologie.
Quali miglioramenti posso aspettarmi dalla terapia con cellule staminali?
I possibili miglioramenti variano a seconda delle caratteristiche specifiche della tua malattia e della tua salute generale. Quando si prendono in considerazione le cellule staminali per la cura dell’artrite reumatoide (AR), i risultati sono influenzati da fattori come la gravità della condizione, il tipo specifico di cellule staminali utilizzate e la salute complessiva del paziente.
Ecco alcuni possibili miglioramenti che potresti aspettarti sottoponendoti alla terapia con cellule staminali per l’AR:
- Riduzione del dolore e dell’infiammazione a livello delle articolazioni colpite. Le cellule staminali possono modulare il sistema immunitario e ridurre l’infiammazione cronica caratteristica dell’AR, alleviando così il dolore.
- Miglioramento della funzione e della mobilità articolare. Questo può tradursi in una maggiore facilità di movimento e una migliore qualità della vita.
- Rallentamento della progressione dell’artrite reumatoide, promuovendo la riparazione dei tessuti e riducendo le risposte infiammatorie.
- Riduzione dell’uso dei farmaci tradizionali per l’AR, come i farmaci antinfiammatori non steroidei (FANS), i corticosteroidi e i farmaci antireumatici modificanti la malattia (DMARD), che possono avere effetti collaterali significativi.
- Miglioramento della qualità della vita, permettendo di svolgere attività quotidiane in modo più attivo e piacevole.
Costo della terapia con cellule staminali per l’artrite reumatoide
Il costo della cura dell’artrite reumatoide con le cellule staminali può variare notevolmente a seconda di diversi fattori, rendendo difficile fornire un prezzo specifico senza considerare le circostanze individuali di ogni paziente. I costi possono variare tra €7.000 e €31.000*. Ecco alcuni fattori chiave che influenzano il costo della terapia con cellule staminali per l’AR:
- Tipo di cellule staminali utilizzate
- Numero di sessioni di trattamento necessarie
- Completezza del piano di trattamento
Prima di procedere con la terapia con cellule staminali, è importante discutere in dettaglio i potenziali costi, benefici e rischi con il proprio medico.
*I prezzi indicati sono indicativi e soggetti a variazioni in base a fattori individuali, inclusa la gravità della condizione e il numero di cellule staminali necessarie. I prezzi sono validi a partire da gennaio 2025.
In conclusione
L’uso delle cellule staminali per l’AR non si limita ad alleviare i sintomi, ma mira anche ad affrontare le cause alla base di questa malattia, aiutando a riparare il tessuto articolare danneggiato e a ripristinarne la funzione. Questo approccio rappresenta un cambiamento significativo rispetto alle terapie convenzionali, offrendo una soluzione più duratura alle problematiche insite dell’artrite reumatoide.
Se ti sei mai chiesto se le cellule staminali possono essere utilizzate per trattare l’artrite reumatoide, sappi che ad oggi rappresentano una vera e propria terapia praticata in campo medico.
Contattaci
Puoi contattare il nostro consulente medico per scoprire i risultati attesi del trattamento con cellule staminali in base al tuo caso, il suo costo, la durata e altri dettagli.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director





