Gout is a type of arthritis that causes excruciating pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, most commonly in the great toe. It can sometimes cause problems with the knee and wrist joints.
This article discusses the potential benefits of stem cell therapy for gout. We will also go over how stem cell for knee gout works and what positive results you can expect from it.
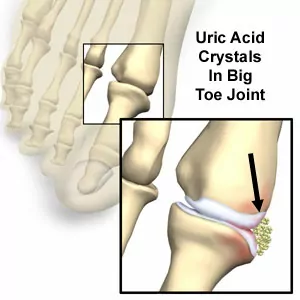
How Does Gout Occur?
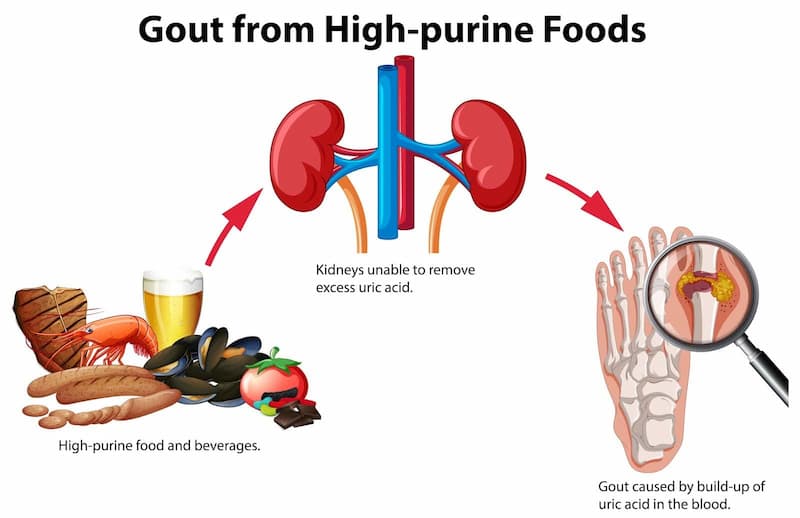
The pathogenesis involved in the development and progression of gout is linked to an increase in uric acid levels in the blood. This accumulation occurs due to the dysfunctional metabolism of excess uric acid in the body. People who consume a high-purine diet are more likely to have elevated uric acid levels.
Some common high-purine foods known to trigger the development of gout include:
- Alcoholic beverages of all types, especially beer
- Vegetables, such as asparagus, cauliflower, peans, dried lentils, and beans
- Whole Grains, such as oats and wheat bran
- Seafood, such as anchovies, herring, mussels, sardines, codfish, scallops, haddock, and trout
- Meats, such as beef, chicken, veal, bacon, turkey, venison and organ meats, including liver
As the level of uric acid in the bloodstream rises, crystals form and are deposited in the joint tissues. Uric acid crystals cause significant joint damage. As a result, patients experience severe pain, difficulty moving the affected joint, and other signs of inflammation such as redness, swelling, and heat.
Regulating uric acid levels in the blood is the primary goal of gout treatment.
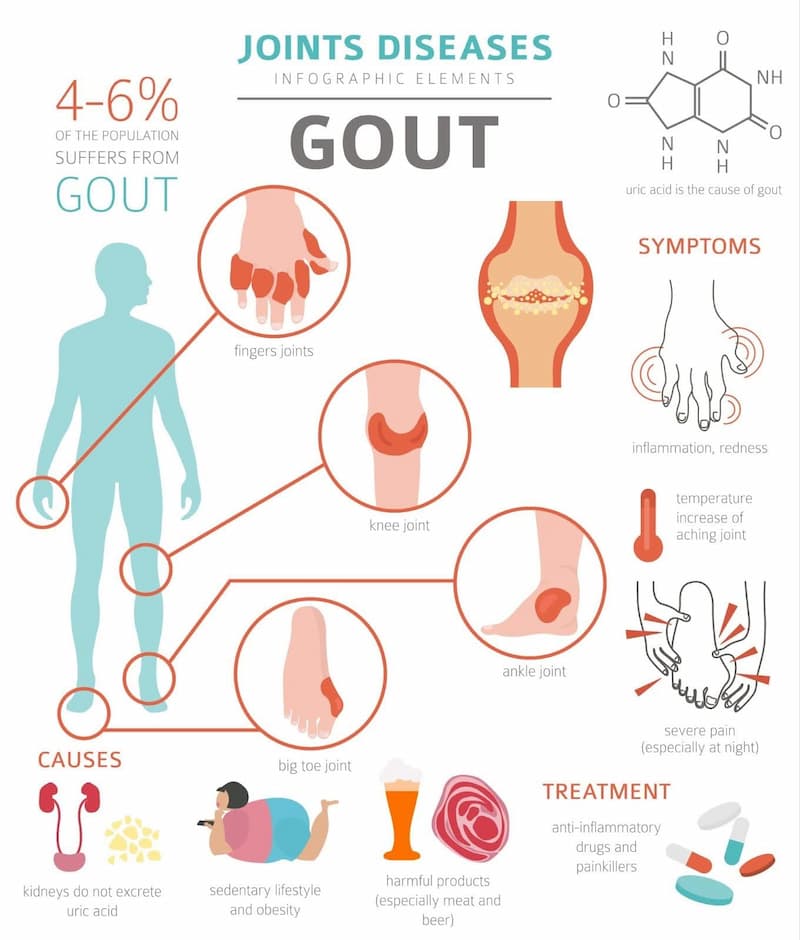
How Is Gout Treated?
Medication for gout is available in two types, each focusing on a different issue:
- If acute symptoms like pain and inflammation are present, it is considered an acute gouty attack. In this case, treatment includes non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine and steroids.
- The second type helps to prevent gout attacks by lowering the uric acid levels in the blood. Allopurinol and febuxostat are medications used to reduce the amount of uric acid produced in the body. Some patients are also treated with other medications, such as Probenecid, which promotes uric acid removal from the body.
In addition, patients are advised to follow a low-purine diet to avoid a rise in uric acid levels.
However, the results of these treatments are often not satisfactory. Patients often complain of recurring gout attacks despite taking these treatments. In addition, joint damage often progresses over a period of time as a result of frequent attacks.
Stem cell therapy for gout has shown immense promise in the management of this condition. This treatment works by promoting the regeneration of new cells in the affected joints. This can inhibit joint damage and restore normal movement, thereby improving the prognosis.
How Do Stem Cells Work in Patients with Gout?
Stem cells possess regenerative properties. These cells are typically received from a donor’s body and transplanted into the patient’s body. Once infused, stem cells migrate to the affected area. This effect can be attributed to stem cells’ chemotactic properties, which allow them to move to the damaged area more easily.
Once the infused stem cells reach the damaged tissues, they begin to produce growth factors and adhesion molecules. Stem cells also cause an anti-inflammatory effect and promote regeneration of articular cartilage, as well as help normalize blood pressure and improve metabolic syndrome, which is often combined with gout.
Stem cell therapy for knee’s gout also works by producing anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects. These properties of stem cells help reduce inflammation and regulate immune system functions. This can reverse joint damage, promote healing, and inhibit further disease progression by lowering the release of pro-inflammatory markers by the immune system.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
What Does Stem Cell Therapy Involve?
Before beginning stem cell therapy for gout at Swiss Medica, our patients must undergo consultations and tests to determine whether the treatment will be beneficial.
Our regenerative medicine specialists plan and carry out the transplantation of stem cells derived from the donor’s body into the patient’s body to aid in the regeneration of new, healthy cells.
Following that, the doctor may prescribe medications or other procedures, such as IMR therapy and physiotherapy.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Painful?
Stem cell therapy is usually painless. Patients may experience minimal pain commonly associated with injections. Your stem cell expert at Swiss Medica Clinic might administer local anesthesia during the procedure to maximize your comfort and help you avoid pain.
Additional Therapies to Improve the Results
Stem cell therapy needs to be combined with conventional treatment, such as medication and a low-purine diet, to improve and sustain the results. This is one of the essential aspects of gout treatment, as a high purine diet can keep uric acid levels elevated, causing patients to experience frequent gout attacks in the future.
Hence, it is essential to emphasize the need to follow a low-purine diet to sustain the positive results of stem cell therapy.
In addition, patients are advised to maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and follow a special diet with purine-low food to normalize the balance of purines. This can help regulate metabolism, enhance joint health, and minimize the risk of future attacks in patients undergoing stem cell therapy for knee’s gout and other types of this condition.
Safety of Stem Cell Therapy in Gout Treatment
Stem cell therapy is generally considered safe for patients with gout. At Swiss Medica, we harvest mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cords and placentas in a sterile environment to reduce the risk of contamination. These tissues are discarded following childbirth, making the harvesting process ethically simple and non-invasive. Hence, the risk of side effects is minimal.
At Swiss Medica, we take quality control to the next level by thoroughly inspecting each stem cell product multiple times before administering it to a patient. Our in-house laboratory provides us with the flexibility to closely monitor the composition and viability of the stem cells, ensuring that every dose meets the highest standards of both safety and efficacy.
Possible Results of the Therapy
Patients can expect significant improvement in their symptoms, including joint pain and swelling, after stem cell therapy. They can also expect a substantial decline in the frequency and severity of gout attacks.
Some positive effects of stem cell therapy for knee’s gout and other types of this condition include:
- Relief from pain, inflammation, and soreness within the first few days after the stem cell injection.
- Improvement in the range of movement in the affected joint.
- Normalized blood pressure.
- Increase in energy level.
Are There Any Side Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Gout?
No severe side effects are reported during laboratory research or clinical treatments in patients during stem cell therapy for gout. Some patients may experience mild side effects such as fever, pain, redness, and fatigue. They are frequently temporary and disappear within a few days.
The Advantages of Our Treatment System
Stem cell therapy for gout can help reduce painful symptoms and increase the range of mobility of the affected joints. It occurs due to the anti-inflammatory properties of stem cells, which can reduce inflammation in the joints and allow them to move freely.
This allows patients to feel improvements in joint movement within a few days of their first session. The anti-inflammatory effect of the treatment lasts nearly two to three months, with most patients seeing a significant improvement in their condition over time.
Patients may experience less pain and return to a normal quality of life if they combine more traditional methods of therapy, such as a healthy diet, exercise, IMR therapy, and physiotherapy. During our treatment program, doctors will recommend some of these methods and prescribe medications to achieve more consistent results.
How to Enter the Stem Cell Therapy Program
You can contact our stem cell experts at Swiss Medica Clinic to learn more about our treatment program and the possible outcomes you can expect from it.
Here is a breakdown of the application process at Swiss Medica.
Initial Consultation
Our experienced medical advisors will discuss your medical history, health concerns, and treatment goals, providing detailed information about our stem cell therapy for gout programs.
Free Medical Evaluation
Our team of skilled physicians will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including reviewing your records, diagnostic tests, and consulting specialists to develop the most appropriate treatment plan.
Personalized Treatment Plan
Based on the medical evaluation, our physicians will create a tailored treatment plan, including stem cell therapy for gout and complementary therapies, to optimize your outcomes.
Free Consultation with a Regenerative Medicine Expert
During your free consultation, our regenerative medicine specialists will assess your condition, answer any questions you may have, and provide expert guidance on potential treatment options.
Convenient Treatment Scheduling
We’ll work with you to schedule your treatment sessions at our facility, providing guidance and support to ensure a stress-free experience.
Transparent Pricing and Arrangements
We’ll provide a detailed breakdown of the final pricing and assist with any logistical arrangements, such as travel accommodations and local transportation.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Gout
The cost of stem cell therapy for gout depends on the extent of joint damage, the duration and severity of the condition, the patient’s age, general health, and other conditions that could potentially aggravate the symptoms. It usually ranges from €7,000 to €25,000.
Schedule a free online consultation with our regenerative medicine specialists to discuss your condition and explore personalized treatment options.
Send a request
Contact us to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Dalbeth, N., Choi, H. K., Joosten, L. A. B., Khanna, P. P., Matsuo, H., Perez-Ruiz, F., & Stamp, L. K. (2019). Gout. Nature reviews. Disease primers, 5(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0115-y
Hainer, B. L., Matheson, E., & Wilkes, R. T. (2014). Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of gout. American family physician, 90(12), 831–836. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25591183/
Medina, J. P., Yáñez, R., Mediero, A., & Largo, R. (2023). MSC therapy ameliorates experimental gouty arthritis hinting an early COX-2 induction. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1193179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1193179
Lopez-Santalla, M., Fernandez-Perez, R., & Garin, M. I. (2020). Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment: An Update on Clinical Applications. Cells, 9(8), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081852
Gao, F., Chiu, S. M., Motan, D. A., Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Ji, H. L., Tse, H. F., Fu, Q. L., & Lian, Q. (2016). Mesenchymal stem cells and immunomodulation: current status and future prospects. Cell death & disease, 7(1), e2062. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.327
Jiang, W., & Xu, J. (2020). Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell proliferation, 53(1), e12712. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12712
Yokose C, McCormick N, Choi HK. The role of diet in hyperuricemia and gout. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 1;33(2):135-144. doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000779
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor







