Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition where the body mistakenly attacks the thyroid, causing inflammation and reduced hormone production. This can lead to symptoms like persistent fatigue, weight changes, brain fog, or mood fluctuations.
Even with standard hormone therapy, symptoms may persist or change from day to day, affecting how patients function and feel. This is why patients may consider regenerative options like stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s. Used along with standard treatment, stem cells may help regulate the immune response and support thyroid regeneration—not as a quick cure, but as a possible way to improve hormone stability.
Understanding Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Why It Develops
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition. This means the body’s own immune cells target the thyroid as if it were a threat. Over time, the thyroid gland tissue is gradually damaged, and as more thyroid cells are destroyed, the gland can no longer produce enough thyroid hormone—leading to hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid).
Hashimoto’s usually develops due to a mix of factors:
- Genetics. A positive family history is common, and the disease often appears alongside other autoimmune conditions.
- Environmental triggers. Long-term stress, past infections, or other immune stressors can disrupt immune balance.
- Hormonal shifts. More common in women, especially during pregnancy, postpartum, or midlife due to significant hormonal changes.
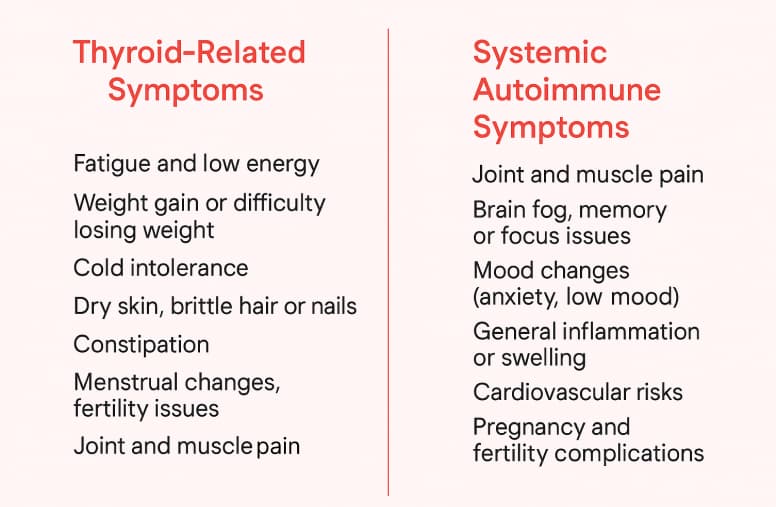
Common Symptoms and Long-Term Risks of Hashimoto’s Disease
Symptoms often develop gradually and can lead to broader issues related to autoimmunity. Early on, they might be attributed to other causes. As thyroid function declines, symptoms typically become more pronounced:
Standard Treatments for Hashimoto’s—and Their Limitations
Typically, doctors focus on correcting the hormone deficiency first, since low thyroid hormones cause the most immediate health issues. Let’s look at the common approaches and their limitations.
| Treatment | Benefits | Limitations |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy |
|
|
| Corticosteroid Therapy |
|
|
Why Conventional Treatment Doesn’t Address the Autoimmune Trigger
Hormone replacement therapy is effective in treating Hashimoto’s symptoms, but it does not address the root cause—the immune system attacking the thyroid. Even with medication, the immune system may continue to produce anti-thyroid antibodies, and lymphocytes may continue to infiltrate the thyroid gland. The inflammation may persist. Over time, this can further reduce thyroid functions.
That is why many patients seek complementary approaches. They may try nutritional changes, supplements, or regenerative treatments for Hashimoto’s to help modulate the immune system.
Can Stem Cell Treatments for Hashimoto’s Disease Help, and How Does It Support Thyroid Tissues?
Stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s disease has been studied in recent years to see if stem cells can function as a repair system and immune system modulator within the body. Rather than targeting one specific immune pathway, stem cells for autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s have a broader, balancing effect.
Types of Stem Cells for Hashimoto’s Disease
Based on Hashimoto clinical trials, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are considered among the most promising and well-tolerated cell-based therapies being investigated for immune regulation and thyroid support. These adult cells (derived from healthy postpartum tissues) originate in bone marrow, fat, the umbilical cord, and the placenta. Their therapeutic value stems from the molecules they release, which migrate to inflammation sites, as well as their ability to modulate an overactive immune system.
For Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, stem cells mostly mean donor cells sourced from thoroughly screened umbilical cord or placental tissue.
In our article, you’ll learn about the different types and sources of MSCs and how they are applied in treating complex conditions.
Read moreWhat Stem Cells Do Inside the Immune System: Main Mechanisms
Stem cells for Hashimoto’s disease are known for their ability to regulate the immune system rather than suppress it, as well as to create an environment conducive to thyroid tissue recovery.
Mechanism 1. Modulating Inflammation and Autoimmune Activity
MSCs can calm the overactive immune response. They can help rebalance key immune cells—especially Th17 and Treg, which play a major role in autoimmune attacks. When this balance is restored, the immune system becomes less aggressive.
Also, MSCs can reduce inflammation in the thyroid. They lower the production of inflammatory cytokines (the molecules that drive autoimmune damage), helping the thyroid environment become less hostile.
Mechanism 2. Reducing Antibody Levels (TPO, TgAb) as a Part of Immune System Modulation
Hashimoto’s disease is often monitored by measuring thyroid antibodies in the blood—anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) and anti-thyroglobulin (TgAb) antibodies. By calming the immune system, the production of these antibodies may decrease.
Results: Regenerative Potential for Thyroid Tissue
After entering the bloodstream, MSCs can “home in” on the thyroid, guided by signaling molecules and adhesion proteins. Once there, they release factors that reduce immune infiltration and help lessen tissue damage. It does not imply that stem cells for Hashimoto’s disease can “regrow” the thyroid, but there are studies and patient reports indicating fewer lesions and less scarring compared to untreated thyroids.
The goal of stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s disease is to optimize and protect what remains. It’s an immune-balancing therapy; stem cells cannot fully replace the thyroid.
To learn more about how MSCs support recovery, read our dedicated article. You’ll discover what molecules they release, how they locate damaged tissue, and why they don’t replace cells directly but instead create the conditions the body needs to recover.
Read moreExpected Outcomes—What Results Can Patients Experience after Stem Cell Treatment for Hashimoto’s Disease?
With stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s, outcomes can differ for each individual, depending on factors like how advanced their disease is, their overall health, and how their immune system responds.
| Potential Outcomes for Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis after Stem Cell Therapy | What Improvement Might Look Like |
| Reduction of Symptoms |
|
| Improved Thyroid Function |
|
| Calmer Autoimmune Activity |
|
Get a free online consultation
Explore your options for stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s disease with a free online consultation. Our medical advisor will review your case and medical history, discuss potential outcomes, and determine whether you’re a suitable candidate.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Success Stories and Patient Improvements
At Swiss Medica, a stem cell clinic in Serbia, most patients report better energy levels, a more stable mood, reduced inflammation, fewer autoimmune flare-ups, and improvements in everyday stamina. Here is just one example—more stories you can find on our YouTube.
— A patient from the Netherlands
“Living with Hashimoto’s drained every bit of energy I had. I could barely walk for an hour, and even that felt like too much. My thyroid was so damaged that there was almost no healthy tissue left.
After years of trying medications and research programs with no real progress, I decided to try stem cell therapy. The treatment was comfortable, I had no side effects at all, and the whole process felt safe. Now I’m waiting for the results—and hoping that in a few months I’ll be able to walk longer and enjoy a more active life again.”
Note: Individual responses to stem cell therapy for Hashimoto’s vary.
Who Is a Good Candidate for Stem Cell Therapy for Hashimoto’s?
Candidates are typically those who have been diagnosed with Hashimoto’s disease and are looking for something to supplement conventional treatment.
| Category | Details |
| Disease Severity |
|
| Age |
|
| Exclusions & Cautions |
|
Safety, Side Effects, and Clinical Evidence
Clinical trials for Hashimoto’s with mesenchymal stem cells have shown that MSC therapy is generally well-tolerated. The most common reported side effects are mild and resolve within a day or two: headache, low-grade fever, or brief fatigue. Some patients with autoimmune thyroiditis have reported improvements in symptoms and, in some cases, favorable changes in thyroid-related markers.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in the Management of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Diet and lifestyle adjustments can play a supportive role in Hashimoto’s symptom treatments. While these changes may not replace the need for thyroid hormone pills, they can help patients feel better and possibly calm the autoimmune activity.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Patients explore diets that potentially reduce inflammation, like the autoimmune protocol (AIP) diet, paleo diet, or simply a whole-foods diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Selenium and nutrients: Selenium is a mineral important for thyroid function. Some studies have found that selenium supplementation can modestly reduce thyroid antibody levels in Hashimoto’s patients. Vitamin D is also critical for immune regulation—correcting its deficiency may support the immune system.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances and might be a trigger for autoimmune flare-ups. Better stress management, regular exercise, and a normal sleep cycle may help reduce inflammatory chemicals in the body, thereby restoring thyroid function.
How Stem Cells Compare to Other Advanced Treatments
Here’s a brief comparison of stem cell treatments for Hashimoto’s disease with a few other advanced autoimmune thyroiditis therapies:
| Advanced Hashimoto’s Therapies | Pros & Considerations |
| Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Hashimoto’s | Pros: Potential influence on the immune system; mild side-effect profile; works best in conjunction with standard treatments. Considerations: Results vary; not insurance-covered. |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy | Pros: Effective for stabilizing symptoms. Considerations: May not fully resolve symptoms in all patients. |
| Lifestyle & Functional Programs | Pros: Low risk, holistic, may improve symptoms and antibody levels. Considerations: Results vary; requires consistent effort; may not be enough for moderate or severe disease alone. |
Stem Cell Therapy Procedure at Swiss Medica
Swiss Medica’s goal is to support your whole condition, not just administer stem cells. Here is what your journey with us looks like:
1. Initial Evaluation
We take time to understand your story—your symptoms and history. Our doctors review your labs and may require a thyroid ultrasound to get a clear picture of your current health. Together, our specialists consider whether stem cell therapy is the right fit for you.
2. Treatment Planning
Your treatment plan is created specifically for you. It outlines the type of MSCs, the number of infusions, and the supportive therapies that can help you feel your best.
3. Stem Cell Administration
Stem cells are given through a gentle IV infusion, similar to a regular drip. The procedure is comfortable, and you’re monitored the entire time.
4. In-Treatment Care
Throughout your stay, our medical team checks on you every day. You continue your thyroid medications and receive supportive therapies—physiotherapy, massage, or Intracellular Metabolism Recovery (IMR), a personalized blend of vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and antioxidants—to help your body respond and recover more smoothly. Plasmapheresis may also be offered in certain complex cases.
5. Follow-Up
Before you leave, we guide you through the next steps: labs, lifestyle recommendations, and medication considerations. Over the following 3–6 months, we stay in touch and check on your progress.

Why Patients Choose Swiss Medica for Stem Cell Treatment for Hashimoto’s Disease
Many patients choose Swiss Medica due to our expertise in autoimmune and neurological conditions, as well as our coordinated care:
- Specialized experience: Our team has 14 years of experience treating autoimmune disorders using cutting-edge regenerative medicine.
- Multidisciplinary team: Each patient is cared for by a team that includes regenerative specialists, physiotherapists, and neurologists.
- Personalized protocols: Treatment plans are tailored—cell source, dose, and supportive therapies are adjusted to your specific condition and needs.
- Supportive environment: Staff assist with airport pickup and daily needs, creating a calm and attentive setting during treatment.
- Safety: To ensure product viability and safety, our in-house lab adheres to strict protocols and GMP standards.
- Positive track record: 10,000+ patient reports of symptom improvements.
- Accessible location: Our newly built Belgrade hospital provides high-quality care at a lower cost than Western Europe or the United States.
- Continued follow-up: Regular check-ins after you return home, ensuring long-term support.
Skilled doctors, comfortable spaces, nutritious food, and an in-house lab that meticulously prepares each cell product are the benefits that Hashimoto’s patients enjoy at Swiss Medica.
Costs and Availability
The cost of stem cell therapy varies based on program length, number of infusions, cell type, included therapies, diagnostic needs, and accommodation details.
| Region | Typical Cost of Stem Cell Treatment for Hashimoto’s |
| United States | $15,000–$30,000+ |
| Europe | €10,000–€40,000 |
| Serbia (Swiss Medica) | €7,000–€31,000* |
*Prices are indicative and based on 2026 estimates; they may vary depending on condition severity and required cell quantity.
Ready to Start Your Treatment Journey? Contact Our Clinic
Managing Hashimoto’s can be overwhelming, but you don’t have to face it alone—our medical team is here to help you explore whether stem cell treatment for Hashimoto’s disease could be the right next step.
Contact us
Book a free online consultation today to discuss your symptoms, review your medical history, and receive personalized guidance on your treatment options.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Hashimoto’s be cured with stem cells?
No, Hashimoto’s cannot be cured with stem cells. Stem cells may reduce autoimmune activity, lower inflammation, and improve symptoms for some patients.
2. Will I be able to stop taking thyroid hormone after treatment?
Some patients may need a lower dose if their thyroid function improves after therapy.
3. How long might it take to notice changes in my symptoms or lab results?
Patients often notice symptom improvements within 1–3 months, with lab changes typically becoming clearer between 3–6 months.
List of References:
Kaur J, Jialal I. Hashimoto Thyroiditis. [Updated 2025 Feb 9]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459262/
Markomanolaki ZS, Tigani X, Siamatras T, Bacopoulou F, Tsartsalis A, Artemiadis A, Megalooikonomou V, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C. Stress Management in Women with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Mol Biochem. 2019;8(1):3-12 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31404454/
Wang, Y., Yi, H. & Song, Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 12, 545 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x
MD, Physician in General Medicine, Gastroenterology, Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Cardiology. Regenerative specialist