Stem cell therapy stands out as the most promising treatment intervention in regenerative medicine. Stem cells have not only transformed technology, offering infinite therapies and curative treatments for major life-threatening diseases, but they are a breakthrough in modern science and medicine as well.
These cells have shown a remarkable ability to aid in repairing damaged cells or organs in patients suffering from fatal diseases and injuries. Examples include some vexing conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, spinal cord injuries, diabetes, etc.
However, is it true that there are many more diseases that stem cells can cure? And how are stem cells used to treat diseases? In this article, we will look into their clinical applications and their advantages over traditional treatment options.
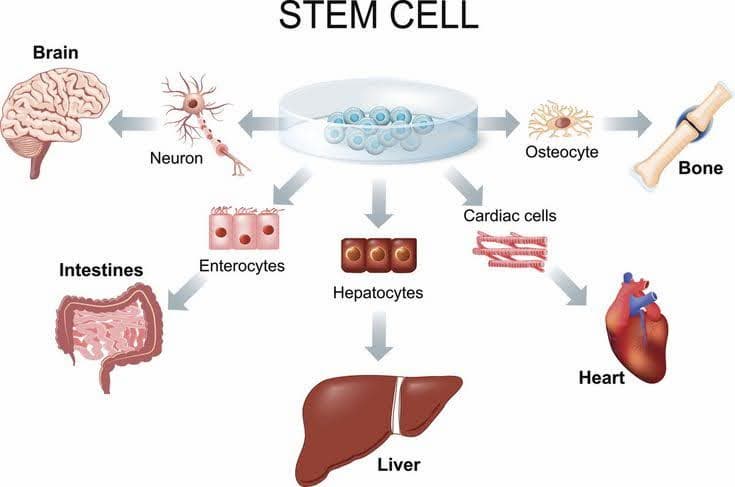
Stem Cell Therapy
How do stem cells cure diseases? Can it truly be considered a miraculous cure capable of shielding us from threatening health conditions and the effects of aging?
Before we provide you with a list of diseases treated by stem cells, it’s important to first understand the fundamental nature of stem cells and their key properties.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found within living organisms. They are famous for their potential to divide, replenish, and mature into specialized human cell types that can be used to construct various tissues, cells, and organs within the body. The four types of stem cells are:
- Embryonic stem cells (ESCs).
- Adult stem cells.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
- Perinatal stem cells.
Stem cell therapy is a regenerative medicine approach that utilizes stem cells, including embryonic cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells, to treat and prevent diseases and injuries.
MSC’s Mechanisms of Action
MSCs, or mesenchymal cells, are a type of adult stem cells that can be found in bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, etc. Their unique regenerative and therapeutic properties make them the best choice for treating several conditions.
When injected, MSCs differentiate into specialized cells, allowing tissue repair and cell regeneration. Both direct differentiation and paracrine signaling (when a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering their behavior) are important mechanisms by which stem cells can contribute to tissue regeneration and disease treatment.
Moreover, their immunomodulatory properties allow stem cells to regulate the immune system for treating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Clinical Applications of MSCs
Neurological disorders and cardiovascular conditions are not the only ones among health problems and diseases treated by stem cells. MSCs offer potential treatments for a wide range of health conditions.
A list of diseases treated by stem cells includes:
- Orthopedic conditions
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Neurological disorders
- Autoimmune diseases
- Graft vs. host diseases
- Liver diseases
- Lung disorders
- Sport injuries
It is critical to recognize that while there are several diseases that can be treated by stem cells, ongoing research is essential to optimize their efficacy, and safety, and establish standardized protocols for clinical use.
How Do Stem Cells Cure Diseases: Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapies can utilize either autologous (the patient’s own cells) or allogeneic (donor-derived) stem cells. Each approach offers key advantages, such as:
- Stem cells have unique regenerative abilities to differentiate into various cell types and replace damaged cells and tissues.
- Stem cells can be driven from various sources within the body, with varying advantages and applications, promoting versatility in treatment options.
- Autologous stem cell therapy offers a reduced risk of immune rejection because it uses the patient’s own stem cells.
- Stem cell therapy is a personalized treatment based on needs, conditions, allowing for more effective treatment.
- Stem cells offer minimally invasive procedures, reducing the risks involved in invasive surgeries and allowing for longer recovery times.
- Stem cells allow for the treatment of neurodegenerative and autoimmune diseases that were once considered untreatable.
- Stem cell therapy promotes disease modification by targeting the underlying cause of the condition rather than managing symptoms.
Contact us
You can receive detailed information about the use of stem cell treatment for your case >>>
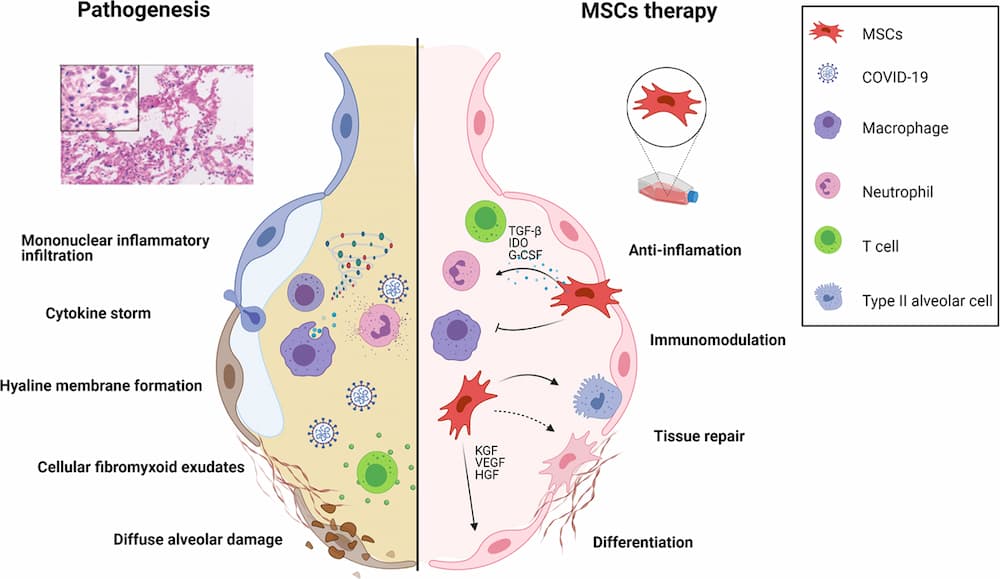
What Diseases Are Treated With Stem Cells?
What can human stem cells be used to treat? Stem cell research, a multidisciplinary field, is dedicated to exploring the applications of these cells in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, drug discovery, and beyond. It does so by learning the biology of stem cells and developing new methods for their isolation.
Stem cell research is rapidly evolving, constantly expanding the list of diseases treated by stem cells:
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune disease caused by an immune system’s aggression over the protective covering of the nerve fibers. Stem cells can help relieve MS symptoms by differentiating into multiple specialized cells and promoting tissue repair, all while modulating the immune system. The most commonly used stem cells for treating MS are adult mesenchymal stem cells.
Cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular diseases involve disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels. This includes coronary artery diseases, heart failure, hypertension, stroke, peripheral artery disease, etc. By harnessing stem cells’ regenerative properties, most cardiovascular diseases can be treated by intravenous (IV) infusions of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
The mechanism of action of stem cells in cardiovascular diseases includes:
- Heart tissue regeneration.
- Angiogenesis effects.
- Anti-inflammatory effects.
Diabetes and diabetic ulcers
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high sugar levels in the blood due to inadequate production of insulin, ineffective use of insulin by the body cells, or a combination of both.
Diabetes can lead to different complications, including a high risk of ulcers in the lower limbs due to cardiovascular and neurological changes, as well as a deficit in wound healing. Stem cells can promote wound healing by releasing growth factors that stimulate tissue regeneration and angiogenesis.
Stem cells used to treat diabetes and ulcers are:
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
- Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs)
- Bone marrow-derived stem cells
Autism
Stem cells, particularly MSCs, have been found to potentially treat the pathophysiological mechanisms of autism spectrum disorder, thus making the symptoms less severe, for instance:
- Stem cells help replace damaged or dysfunctional cells and restore brain functions.
- Stem cells help modulate the brain, promote neural growth and synaptic activity, and reduce inflammation or oxidative stress.
- Stem cells help modulate the immune system.
Liver diseases
Liver diseases primarily affect the liver structure and its functions, leading to liver dysfunction, impaired metabolism, toxin accumulation, and, in severe cases, liver failure.
Due to stem cells’ remarkable regenerative capacity and ability to differentiate into liver cells, they are considered the most effective treatment. The stem cells most commonly used for the therapy are MSCs.
Crohn’s disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the digestive tract. It is characterized by inflammation and is believed to be a result of genetics, environment, and immunological factors. Stem cells are being explored as a potential treatment for this disease, particularly where traditional therapies are ineffective or have caused significant harm.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder linked to abnormalities in pain processing and perception. The symptoms can include:
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Fatigue
- Sleep issues
- Mood issues
- Cognitive difficulties
Stem cells, particularly MSCs, have been found to release anti-inflammatory effects to reduce damaged cells and reduce inflammation and pain involved in fibromyalgia.
Parkinson’s disease
This neurodegenerative disorder affects movements, with symptoms worsening over time. Stem cells have shown promising results in treating Parkinson’s by replacing the dopamine-producing nerve cells, lost as a result of the disease. The type of stem cells typically used for treating Parkinson’s is mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
Injuries and Musculoskeletal pain
Stem cells are a promising approach to treating injuries and musculoskeletal pain. Let’s take a look at the mechanism of action of stem cells in injuries:
- Stem cells can differentiate into any cell type, including bone, cartilage, muscle, and tendon cells. They promote tissue regeneration to repair and help restore structural integrity and functions of the affected tissues.
- Stem cells reduce inflammation by modulating immune system response and reducing inflammation in the affected areas.
- Stem cells secrete growth factors and cytokines that stimulate the production of new blood vessels to support the body’s healing process.
- Stem cells modulate pain pathways in the nervous system, meaning they help alleviate musculoskeletal pain.
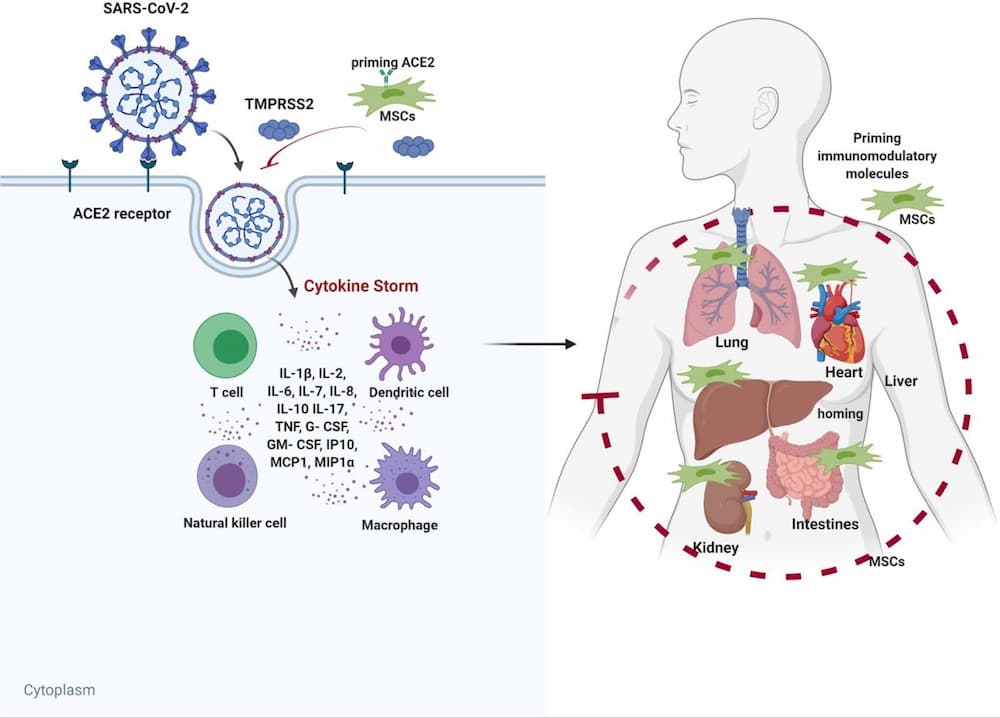
COVID-19
COVID-19 primarily affects the respiratory system and can be characterized by fever, cough, loss of taste and smell, congestion, nausea, and diarrhea. Stem cells help treat the disease via:
- Modulating the immune response by suppressing the proinflammatory cytokines and promoting anti-inflammatory factors, preventing further damage to lungs and other organs
- Promoting tissue repair and regeneration
- Releasing anti-inflammatory factors
Contact us
Find out whether you would benefit from stem cell treatment in your case >>>
Can Stem Cell Therapies Stimulate the Formation of Tumors?
The chances of stem cell therapies leading to tumor formation depend upon various factors, such as:
- Type of stem cells used.
- Method of administration.
- Characteristics of the recipient
Certain types of stem cells to treat diseases, particularly embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells, can lead to a non-controlled multiplication that elevates the risk of the formation of tumors, if not controlled properly. Furthermore, viral vectors or genetic manipulations to modify stem cells can also cause genetic abnormalities, increasing the risk of tumor formation.
However, not all stem cell therapies carry the risk of tumor formation because these risks are mitigated through rigorous preclinical testing, careful monitoring of patients, and regulatory oversight.
For instance, MSCs are generally considered the safest option for therapies due to their limited differential potential. Hence, the use of stem cells to treat diseases holds great promise for revolutionizing medical treatment.
Is There a Chance of Immune Rejection With Stem Cells?
Stem cells do pose a risk of immune rejection, especially allogeneic ones, meaning the ones derived from a donor other than the recipient. However, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to suppress the immune response and promote tolerance, making them highly suitable for allogeneic transplantations.
Research results indicate that MSCs have unique properties that allow them to avoid allogeneic rejection:
- MSCs are “hypoimmunogenic”, often lacking expression of MHC-II and costimulatory molecules that trigger immune responses.
- MSCs can modulate the function of immune cells like T cells, dendritic cells, and NK cells, suppressing their activation and proliferation.
- MSCs can create an immunosuppressive local microenvironment through the secretion of factors.
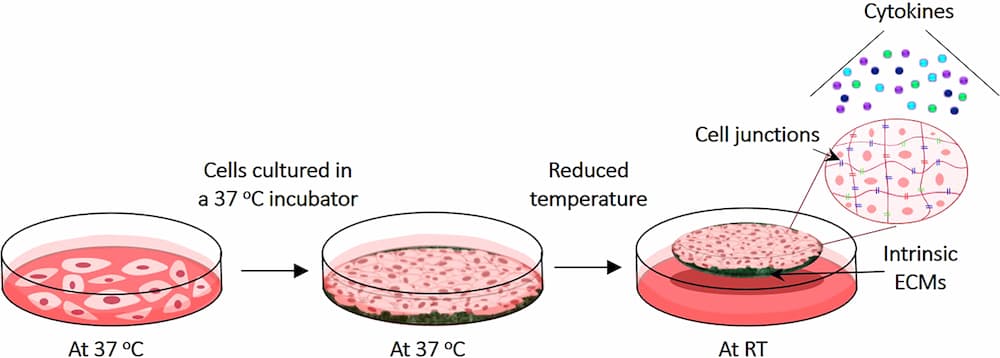
What Does Stem Cell Cultivation Look Like?
In stem cell cultivation, scientists follow special protocols and create environments for optimal conditions, such as:
- Selecting a suitable cultural medium containing nutrients, growth factors, hormones, and signaling molecules to support stem cell growth.
- Maintaining controlled environments, i.e., cell culture incubator, to ensure the survival and growth of stem cells.
- Controlling the density of the cells within the culture to optimize growth and maintain special characteristics of the cells.
- Replenishing nutrients and removing waste products from the culture to maintain optimal growth conditions.
- Regular monitoring of the cultures to spot contamination, cell death, or differentiation.
- Scientists may use specialized techniques as well to manipulate cell cultures depending on the specific goals.
In discussions surrounding the potential applications of regenerative medicine, a frequently posed question is: “Which diseases can be treated with stem cells?”
Stem cells, as the body’s fundamental building blocks, harbor therapeutic potential for some of humanity’s most perilous diseases that were once deemed incurable, and the list of treatable conditions continues to expand. It offers hope for many people around the world and further ignites optimism for the future of medical treatment.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to discover the results you can expect from stem cell treatment >>>
List of References:
Blau, H. M., & Daley, G. Q. (2019). Stem cells in the treatment of disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, 380(18), 1748–1760. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra1716145
Aggarwal, S., & Pittenger, M. F. (2005). Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood, 105(4), 1815–1822. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-04-1559
Martino, G., Franklin, R. J., Evercooren, A. B., & Kerr, D. A. (2010). Stem cell transplantation in multiple sclerosis: current status and future prospects. Nature Reviews Neurology, 6(5), 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.35
Aly, R. M. (2020). The current state of stem cell-based therapies: an overview. Stem Cell Investigation, 7, 8. https://doi.org/10.21037/sci-2020-001
Brito, A., Russo, F. B., Muotri, A. R., & Beltrão-Braga, P. C. B. (2017). Autism spectrum disorders and disease modeling using stem cells. Cell and Tissue Research, 371(1), 153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2685-x
Dalal, J., Gandy, K. L., & Domen, J. (2012). Role of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in Crohn’s disease. Pediatric Research, 71(2–4), 445–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/pr.2011.56
Arenas, E. (2002). Stem cells in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Research Bulletin, 57(6), 795–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0361-9230(01)00772-9
Esquivel, D., Mishra, R., Soni, P., Seetharaman, R., Mahmood, A., & Srivastava, A. (2020). Stem cells therapy as a possible therapeutic option in treating COVID-19 patients. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports, 17(1), 144–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10017-6
Haworth, R., & Sharpe, M. (2020). Accept or reject: The role of immune tolerance in the development of stem cell therapies and possible future approaches. Toxicologic Pathology, 49(7), 1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623320918241
Ryan JM, Barry FP, Murphy JM, Mahon BP. Mesenchymal stem cells avoid allogeneic rejection. J Inflamm (Lond). 2005 Jul 26;2:8. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-2-8. PMID: 16045800; PMCID: PMC1215510.






