As traditional neurologic procedures and medications often fall short in addressing complex autism aspects, many parents are exploring cell-based options as a complementary or alternative approach to improve the life quality of their children with ASD. That’s why stem cell therapy for autism and success rates after this procedure have become topics of large interest.
In this article, we explore just how effective stem cell therapy is for autism—and what real-world clinical outcomes tell us about its success.
Understanding the Role of Stem Cells in Autism Care
Stem cell therapy for autism is a treatment designed to support neurological function and modulate the immune system in children with autism. Medications target only the symptoms; this therapy can address some of the underlying imbalances that lead to the condition.At Swiss Medica, treatment is based on the mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs)—adult, multipotent cells derived from ethically sourced umbilical cord tissue and placental tissue. These cells are known for their strong neuroprotective, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory functions.
Stem cell therapy is not a cure for autism, but it may help improve specific symptoms and enhance quality of life, especially when used in combination with other therapies.
How Stem Cells Influence Brain Function in Autism
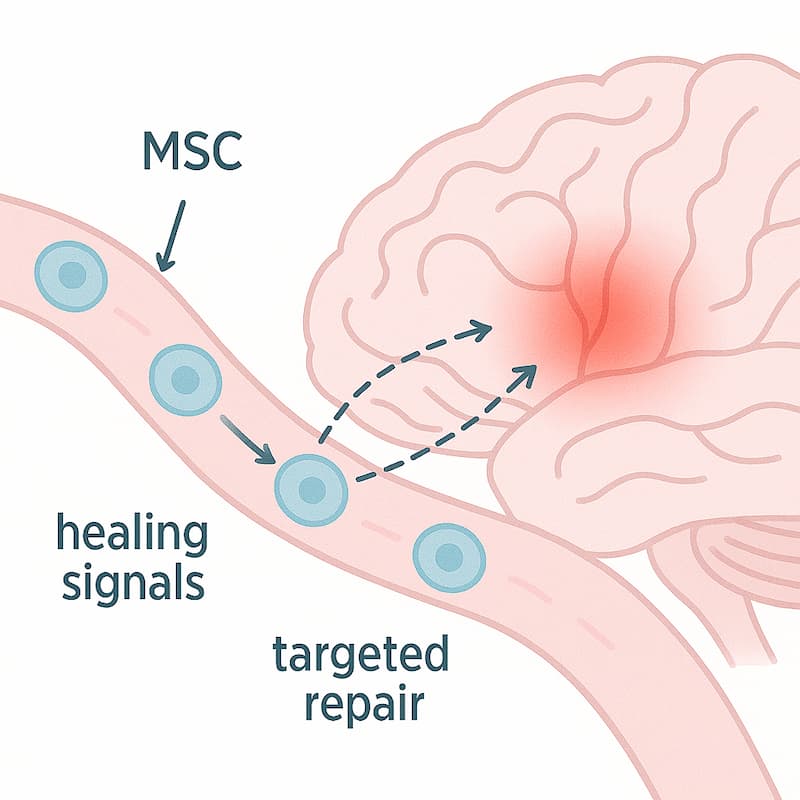
Stem cell therapy for autism supports the body’s natural repair mechanisms through a series of indirect yet powerful biological effects. MSCs do not transform into neurons or replace damaged brain cells; instead, they can influence the surrounding tissues to reduce inflammation, regulate immune response, and promote support of neural system.
Targeting Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation
A growing body of research shows that children with autism often have chronic inflammation in the brain and imbalances in immune response. MSCs help restore balance by:
- Reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels.
- Increased activity of regulatory immune cells.
- Shifting the environment from pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory.
This may help decrease symptoms linked to neuroinflammation, such as irritability, sensory issues, and behavioral instability.
Enhancing Neuronal Connectivity and Repair
In parallel, MSCs secrete neurotrophic factors—molecules that support neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, and circuit repair. This can increase:
- Communication between brain regions
- Processing of social and emotional cues
- Memory and learning capacity
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in Children: What Swiss Medica Offers
The therapy protocol is built around the use of donor-derived mesenchymal stromal cells—adult, non-embryonic cells ethically obtained from placental and umbilical cord tissue.
These cells are selected for their ability to reduce neuroinflammation, modulate immune function, and support repair processes in the brain, all of which are believed to contribute to autism symptoms.
Cell Types Used in Therapy
Our approach includes the following cell-based and supportive biological components:
- Allogeneic MSCs (placental/umbilical origin): Act as the core therapeutic agents due to their immunomodulatory and neuroprotective properties.
- Exosomes: Tiny vesicles derived from MSCs that transport molecular signals into damaged brain regions. These are used both during inpatient treatment and as part of at-home maintenance therapy.
- M2 macrophages: Immune cells used in select cases (based on doctor evaluation) to help balance immune responses and promote neural tissue recovery.
Together, these components aim to enhance brain connectivity, reduce chronic inflammation, and create a healthier neurological environment in children.
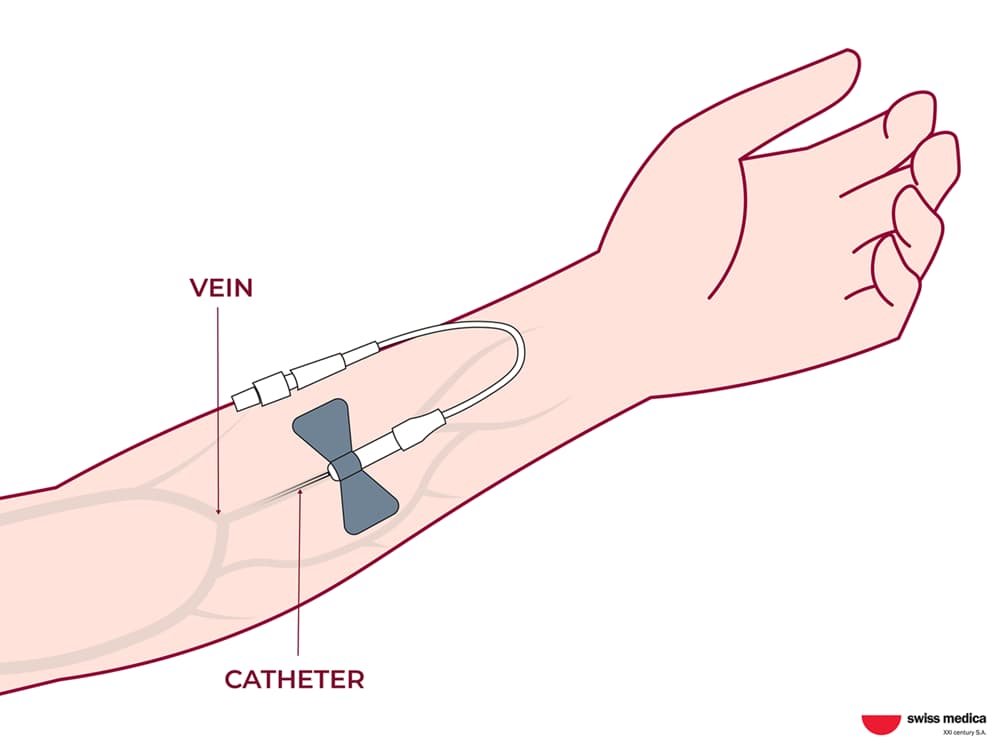
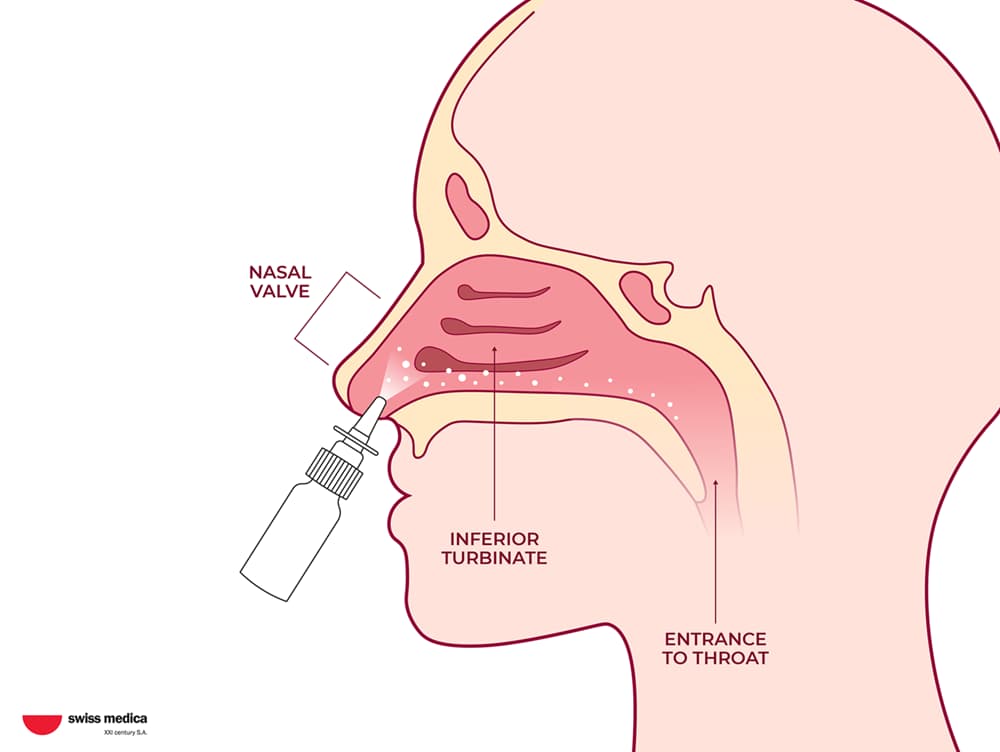
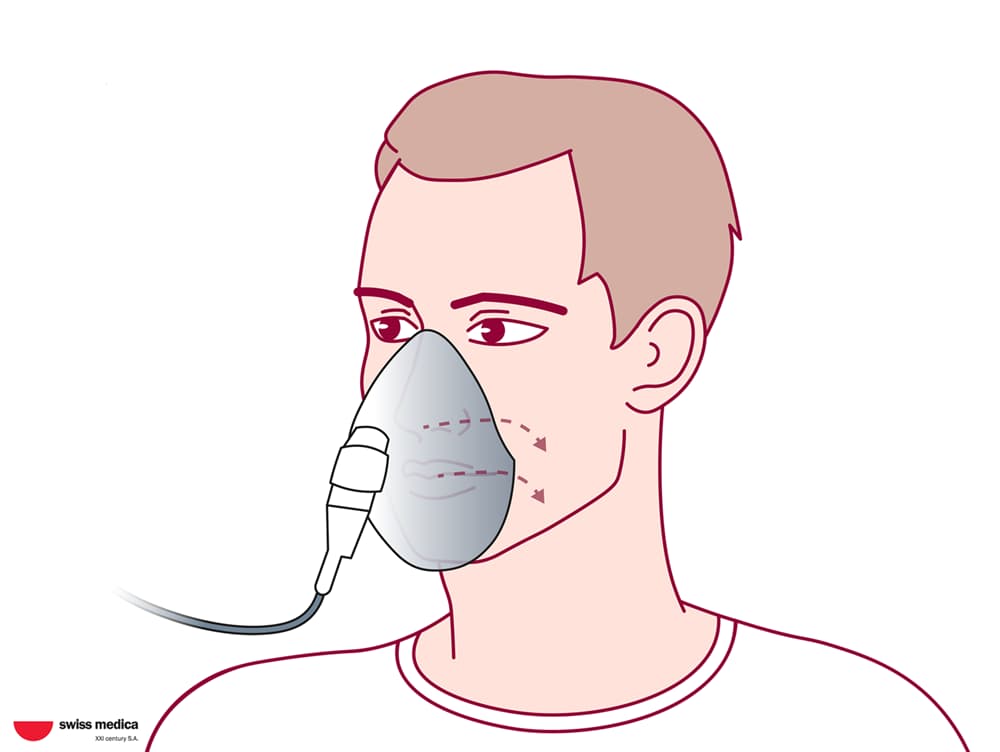
Cells are administered through intravenous infusions, and, in some cases, additional delivery methods may be used (such as nasal sprays or local applications) to target specific systems.
Looking at Outcomes: How Successful Is Stem Cell Therapy for Autism?
Over the past decade, stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising area of research for children with autism. A growing number of observational studies help answer an important question: “How successful is stem cell therapy for autism?”
Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for Autism: Clinical Findings at Swiss Medica
Swiss Medica recently conducted a comprehensive clinical trial with 185 children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). A subgroup of 30 patients underwent detailed behavioral assessments at baseline and 3–9 months after therapy, helping us better understand stem cell treatment for autism, its success rate, and which symptoms are most likely to respond.
According to the study:
- 93.4% of participants in the detailed group showed improvement in at least one symptom.
- 83.3% experienced improvement in half or more of the assessed symptoms.
Most commonly improved areas included
| Stem Cells in Autism: Results | % of Reporting Changes |
| Better eye contact and attention | 57.1% |
| Improved verbal communication | 55.6% |
| Increase attention and focusing | 56% |
These figures help illustrate the success rate of stem cell therapy for autism observed in real-world treatment programs like Swiss Medica’s.
Swiss Medica emphasizes that therapy outcomes depend on numerous factors, including genetics, environment, previous interventions, and co-occurring conditions. We do not claim uniform success across all cases.
Stem Cell Therapy in Autism: Before and After. How Does It Affect Core Symptoms?
Speech and Communication
One of the most consistently reported improvements following cell therapy is enhanced verbal expression. Some children begin to form simple sentences or expand vocabulary within weeks of treatment. These improvements can often be strengthened when stem cell therapy is combined with speech therapy for autism, which reinforces verbal and social development through structured practice.
Another commonly noted benefit is increased engagement with the surrounding world. Children may initiate play, make eye contact more consistently, or respond to social cues that were previously ignored. Results of stem cell therapy for autism, as reported by parents and therapists, often show early improvements within 1–2 months after treatment.
Stereotypic Behaviors
Repetitive actions, such as hand-flapping or spinning, may decrease in frequency or intensity. While some behaviors persist, parents often report that children become easier to redirect and follow daily routines more smoothly.
Hyperactivity and Sleep
Children who were previously hyperactive or prone to night awakenings sometimes experience deeper sleep and more regulated activity levels after intervention.
Get a free online consultation
Interested to know about potential results of stem cell therapy for autism? Fill out the application form below for an online, no-obligation consultation with our regenerative medicine specialist.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
How Long Do Results Typically Last?
Common questions among parents considering cell-based interventions are:
- How long do the effects of stem cell therapy for autism typically last?
- How successful is stem cell therapy for autism in our case?
The initial improvements may emerge within the first few weeks, with the first more noticeable effects of therapy appearing in 2–3 months after treatment.
Does Stem Cell Therapy Work for Autism Regardless of Age?
While stem cell therapy for autism may offer benefits across various age groups, clinical observations consistently show that younger children tend to respond more favorably to treatment. In particular, children aged 3 to 7 years old demonstrate the most significant improvements in areas such as communication, emotional regulation, and cognitive function.
Why Early Intervention Matters
Several factors may explain the enhanced responsiveness among younger patients:
- Neuroplasticity: At earlier stages of development, the brain is more adaptable, with higher potential for forming new neural connections.
- Less entrenched symptoms: Behavioral patterns and comorbid complications are generally less severe and more malleable in younger children.
- Faster biological response: The immune and nervous systems of younger patients may be more receptive to the paracrine signaling mechanisms triggered by MSCs and exosomes.
According to Swiss Medica’s clinical experience, children treated between ages 3 and 7 often begin to show early signs of progress within the first months after therapy, particularly in areas like speech initiation, attention span, and behavioral flexibility.
Potential Risks and Safety of Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
As with any medical intervention, stem cell therapy for autism and its effectiveness must be approached with careful consideration. While clinical observations and emerging studies suggest a favorable safety profile for mesenchymal stromal cells, it’s important to emphasize that the field is still evolving—and ongoing research continues to evaluate both short- and long-term effects.
Is There a Stem Cell Therapy for Autism Without Side Effects?
In stem cell therapy for autism, side effects are rare, mild and temporary, such as:
- A low-grade fever lasting a few hours
- Local discomfort at the injection site
- Short-term fatigue or irritability
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism: A Success Story from One of Our Patients
When evaluating emerging treatments for ASD, including stem cell therapy for autism, success rate is often one of the first factors families research before deciding on next steps.
Swiss Medica has documented multiple before-and-after cases of stem cell therapy for autism, where children demonstrated improved focus and calmer behavior after treatment.
We often publish interviews of parents after stem therapy for autism, as success stories help our future patients.
“After the first stem cell therapy at Swiss Medica in July, we saw incredible changes. He became more independent—getting his own food, eating by himself, and even putting on his shoes for the first time. These may seem like small steps, but for us, they were miracles.
We’ve returned for a second treatment, this time with full confidence. Swiss Medica has given us hope and real progress we never thought possible.”
— A parent from the UK
Get a free online consultation
Ready to learn whether stem cell therapy could help your child?
Contact us today for a free online consultation with one of our regenerative medicine specialists.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Compare to ABA?
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) remains the most widely used and evidence-based behavioral therapy for children with autism. It focuses on improving functional behaviors through structured teaching and reinforcement techniques. But as interest in biomedical approaches grows, many families are asking, “How does stem cell therapy work for autism patients compared to ABA?”
Different Tools, Different Targets
ABA and stem cell therapy for autism are not direct alternatives—they address very different aspects of the condition:
| Aspect | ABA Therapy | Stem Cell Therapy |
| Focus | Behavioral and cognitive skills | Biological and neurological regulation |
| Method | Behavior modification techniques | MSC infusions and exosome support |
| Duration | Long-term and intensive | From months to years with optional maintenance therapy |
| Onset of Effects | Gradual, over months | Often observed within 3 months |
| Targeted Systems | Learning, social interaction, communication | Immune modulation, neuroinflammation, repair mechanisms |
| Evidence Base | Robust, decades of research | Growing, but still under clinical investigation |
Can They Work Together?
Yes—and in fact, they often complement each other. Many families report the most visible improvements when stem cell therapy is followed by cognitive behavioral therapy for autism, such as ABA, speech, or occupational therapy. For example, after therapy:
- Children may respond faster to ABA prompts.
- They may have better attention and fewer behavioral meltdowns, allowing more productive sessions.
- Increased emotional stability can help improve engagement in social learning tasks.
Stem cell therapy is not intended to replace ABA or other traditional autism therapies. Instead, it can be seen as a supportive intervention that may enhance the child’s capacity to benefit from behavioral programs.
Legal Status and Availability of Stem Cell Therapy in the US & UK
In the United States, stem cell therapy for autism is still regarded as an experimental approach, as no treatment of this kind has received FDA approval for autism spectrum disorder to date. But some research centers that are testing the effectiveness of stem cell therapy for autism have reported encouraging and comprehensive results.
Similarly, in the UK, autism-related stem cell therapy is not available as a licensed treatment.
While early studies show potential benefits, this therapy has not yet received full regulatory approval for autism treatment, and clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes.
Where in the World Is Stem Cell Therapy Offered?
Stem cell therapy for autism is now being offered at specialized medical centers in various countries. However, availability and clinical protocols vary significantly across regions due to differing regulatory standards, ethical policies, and levels of clinical advancement.
When choosing a country for stem cell therapy for autism, success rate is an important consideration—but just as critical are safety standards, physician expertise, and long-term follow-up care.
Countries Where Stem Cell Therapy Is Available
Currently, stem cell-based treatment for autism is most commonly available in:
Serbia—Swiss Medica with comprehensive MSC-based therapy supported by in-house biomedical labs and more than a decade of clinical experience.
Mexico—Several private clinics offer stem cell therapy, often using MSCs or umbilical cord blood cells. Oversight and quality standards can differ significantly between providers.
India—These countries offer broader access, though protocols and product sourcing can vary.
United Arab Emirates and Thailand—Some hospitals offer regenerative programs for neurological conditions, including autism, but typically under research-based models.
Cost and Accessibility of Stem Cell Therapy by Region
The cost of stem cell therapy for autism varies significantly across regions. It is influenced by factors such as the clinic’s location, national regulations, cell sourcing, and the complexity of the treatment protocol.
As stem cell therapy is generally not covered by public healthcare systems, more families are seeking clinically supervised, ethically sourced, and transparent international options. For many, the safety of stem cell treatment for autism and its success rate are central to their decision-making process.
Why Choose Swiss Medica for Autism Treatment?
Swiss Medica is located in Belgrade, Serbia—just a 2-hour flight from most major European cities. The clinic offers a family-oriented environment with:
- A barrier-free facility for children with autism.
- Specialized pediatric accommodations.
- Visa support and logistical assistance for international families.
Our Comprehensive, Patient-Centered Protocol
Unlike clinics that offer only stem cell injections, Swiss Medica provides a multimodal, medically supervised program that includes:
- Initial assessment and diagnostics before stem cell therapy for autism, reviews of patient medical history are necessary steps performed by our highly qualified professionals.
- MSC delivery via intravenous infusion and exosome nasal spray or inhalation.
- Supportive therapies, such as physiotherapy, speech therapy, or metabolic drips.
- Home-based maintenance with nasal sprays (5 bottles of exosomes or macrophage secretome).
- Long-term follow-up and optional booster sessions.
We combine stem cell therapy with regenerative procedures such as plasmapheresis and metabolic support, creating a tailored healing environment for each child.
Swiss Medica’s Inclusive Pricing
Serbia is among the cheapest countries for stem cell treatment, especially for families seeking a medically supervised, full-service experience. At Swiss Medica, in Belgrade, we offer a personalized pricing model based on:
- The child’s diagnosis and medical history;
- The combination of cell products used;
- The need for additional therapies.
Prices typically range from €7,000 to €19,000*. This cost covers the full range of treatment and all essential services, with no hidden fees. This also includes:
- Accommodation for one child and adult;
- Chef-prepared meals, customized to individual dietary preferences;
- Housekeeping and laundry;
- Airport transfers;
- Wi-Fi, TV, and child-friendly environment;
*Prices are indicative, based on January 2025, and may vary with condition severity and cell quantity required.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism and Reviews: What Patients Say
When choosing a clinic for stem cell therapy for autism, reviews play a central role. At Swiss Medica:
- 80% of patients report improvement.
- Over 550 video testimonials are available from real families.
- Parents often highlight better focus, calmer behavior, and new skills emerging after treatment.
Contact us
If you’re exploring stem cell therapy and want to understand whether it’s suitable for your child, our medical team is here to help. Just fill out the form below.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References:
Kern JK, Geier DA, Sykes LK, Geier MR. Relevance of Neuroinflammation and Encephalitis in Autism. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Jan 19;9:519. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00519. PMID: 26834565; PMCID: PMC4717322.
Wang Y, Yi H, Song Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Oct 18;12(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x. PMID: 34663461; PMCID: PMC8522073.
Liang Z, Zhang G, Gan G, Naren D, Liu X, Liu H, Mo J, Lu S, Nie D, Ma L. Preclinical Short-term and Long-term Safety of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231213271. doi: 10.1177/09636897231213271. PMID: 38059278; PMCID: PMC10704945.
Gesundheit B, Hochbaum L, Fetyukhina A, Vorobyev V, Vorobyev N. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Treatment Alleviates Autism Spectrum Disorder Symptoms: A Case Report. Cureus. 2025 May 4;17(5):e83440. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83440. PMID: 40462775; PMCID: PMC12130910.
Price J. Cell therapy approaches to autism: a review of clinical trial data. Mol Autism. 2020 May 24;11(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-00348-z. PMID: 32448347; PMCID: PMC7245880.
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist