Dementia is one of the most challenging neurological conditions of our time. It affects memory, behavior, and the ability to perform daily tasks, gradually robbing people of independence. While current medications can only slow down symptoms, stem cell therapy for dementia represents a new regenerative approach that may help protect neurons, reduce inflammation, and support brain function.
At Swiss Medica, we specialize in safe, evidence-based stem cell programs designed to slow cognitive decline and enhance patients’ quality of life.
Understanding Dementia and Its Challenges
Dementia, despite being more common in the geriatric (elderly) population, can affect all age groups. According to research, this condition can develop due to a wide range of risk factors.
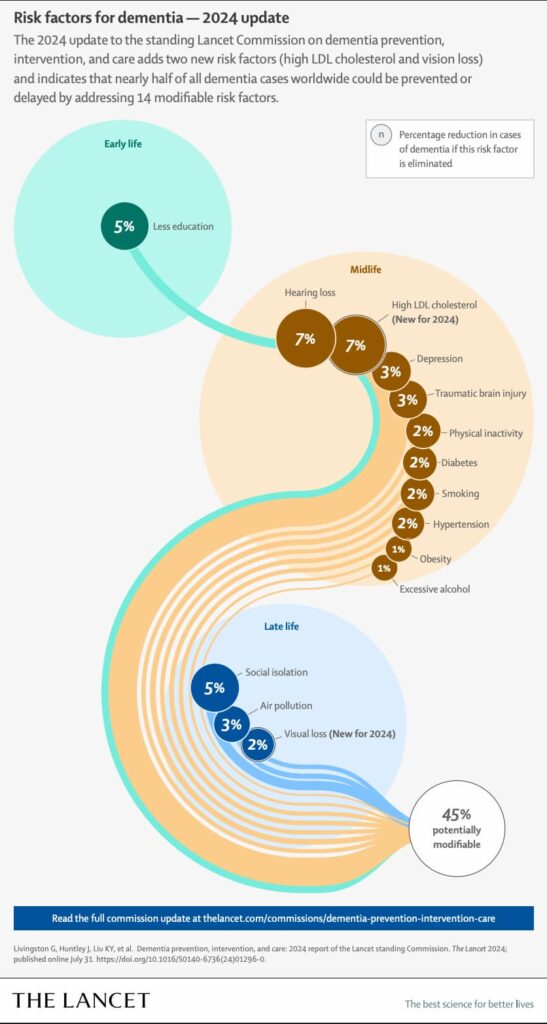
Source: https://www.thelancet.com/pb/assets/raw/Lancet/infographics/dementia-2017/image-1721911723223.pdf
Types of Dementia
Dementia is not a single disease but a group of disorders—most commonly Alzheimer’s, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, and frontotemporal dementia—that gradually damage brain cells and disrupt neural communication.
How Brain Tissue Changes Over Time
As the disease progresses, neurons die, neural connections are lost, and brain tissue shrinks. People experience memory loss, difficulty with decision-making, and changes in mood and emotional control, which affects both independence and family life.
Conventional therapies—such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and lifestyle programs—can temporarily improve symptoms but do not stop degeneration.
That is why scientists and doctors are exploring dementia treatment with stem cells as a way to support the body’s natural repair mechanisms.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works in Dementia
Stem cells are unspecialized cells capable of releasing bioactive molecules that help protect and regenerate damaged tissues. In stem cell treatment for dementia, they act not by replacing dead neurons, but by creating conditions that help the remaining brain cells survive and function better.
Types of Stem Cells Used at Swiss Medica
Our programs use donor mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from umbilical cord and placental tissue—young, biologically active, and ethically sourced. These adult stem cells have powerful immunomodulatory and neuroprotective properties.
In some cases, our doctors may also use the patient’s own (autologous) cells from bone marrow or adipose tissue.
Each batch of stem cells for dementia treatment is tested in our certified EU GMP-grade laboratory for sterility, identity, and genetic stability to ensure safety and minimize stem cell therapy side effects.
Mechanisms of Action
Stem cells help the brain through several biological pathways:
- Neuroprotection: MSCs secrete growth factors that prevent further neuron loss.
- Anti-inflammatory action: They regulate immune responses and calm chronic neuroinflammation, a key driver of dementia progression.
- Regeneration support: By activating local repair processes, they help restore communication between neurons.
- Improved microcirculation: Stem cells promote blood vessel health, improving oxygen and nutrient supply to the brain.
These mechanisms explain why stem cells for dementia are increasingly studied as a tool to support long-term brain health.
Safety, Limitations, and Realistic Expectations
Dementia treatment with stem cells is considered safe when performed in certified clinics using adult MSCs.
At Swiss Medica, safety is ensured at every stage:
- Donor materials come from screened, infection-free placentas and umbilical cords.
- Each product is tested for purity, viability, and genetic stability.
- Personalized dosing avoids vascular overload or immune reaction.
Temporary effects such as mild fever or fatigue may occur within 24 hours after injection.
Limitations:
- The therapy cannot restore lost neurons.
- Outcomes vary depending on disease stage and overall health.
- Maintenance sessions may be needed to prolong results.
Even with these limits, stem cell therapy offers hope for slowing deterioration and improving quality of life.
Can Stem Cells Help with Dementia: Evidence and Clinical Progress
Recent studies show encouraging results for stem cell therapy for dementia patients:
- Slower cognitive decline and improved daily functioning;
- Better attention, focus, and emotional balance;
- Reduced neuroinflammation and improved brain metabolism.
A 2024 Frontiers in Neuroscience review analyzed more than thirty studies and confirmed that mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy improved cognitive test scores and reduced inflammatory markers linked to neurodegeneration.
Сan Stem Cells Cure Dementia?
Current evidence suggests that while stem cells cannot fully restore lost neurons, they can improve the brain’s microenvironment that influences its repair resources.
Recognizing this potential also means understanding safety boundaries and realistic expectations.
Who Can Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy for Dementia
Not every patient with dementia will benefit from stem cell therapy in the same way, which is why a detailed medical evaluation is essential. The treatment shows the best results when started early—before irreversible damage occurs and while the brain still maintains some capacity for repair and adaptation.
Ideal candidates for stem cell transplants for dementia are patients:
- Diagnosed with mild-to-moderate dementia;
- Free from acute infections or active cancer;
- In stable overall health and able to travel;
- Seeking functional improvement rather than a complete cure.
Beyond these medical requirements, our team also evaluates factors such as cardiovascular stability, metabolic balance, and current medications. These can affect how the body responds to regenerative therapy.
Emotional readiness and family support are also important, as positive daily engagement after treatment plays a key role in maintaining results.
Each case is reviewed individually by our medical board. During the consultation, doctors talk about the possible benefits and achievable goals of stem cell treatment for dementia, explaining how the therapy might affect thinking, mood, and everyday activities.
Get a free online consultation
Are you interested in stem cell therapy for dementia? Find out more about your options.
Contact our regenerative specialist.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
The Swiss Medica Treatment Process
Step 1—Consultation and Baseline Evaluation
The process begins with an online or in-clinic consultation. Our neurologists assess medical history, imaging (MRI or CT), and lab tests to confirm eligibility and design a personalized protocol.
Step 2—Stem Cell Preparation and Administration
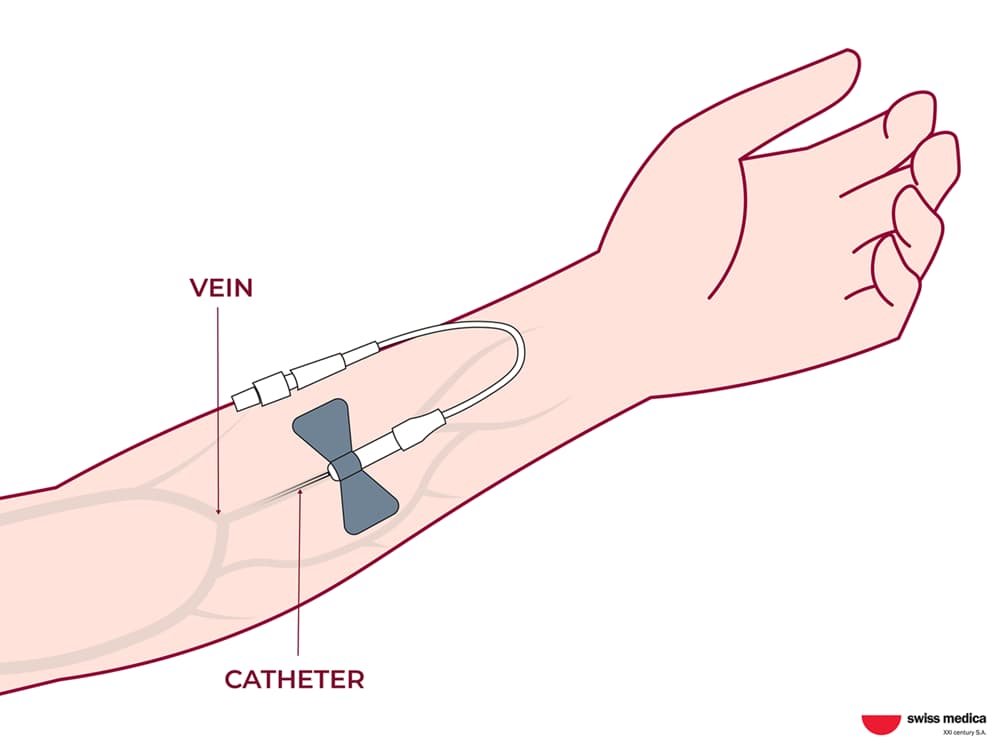
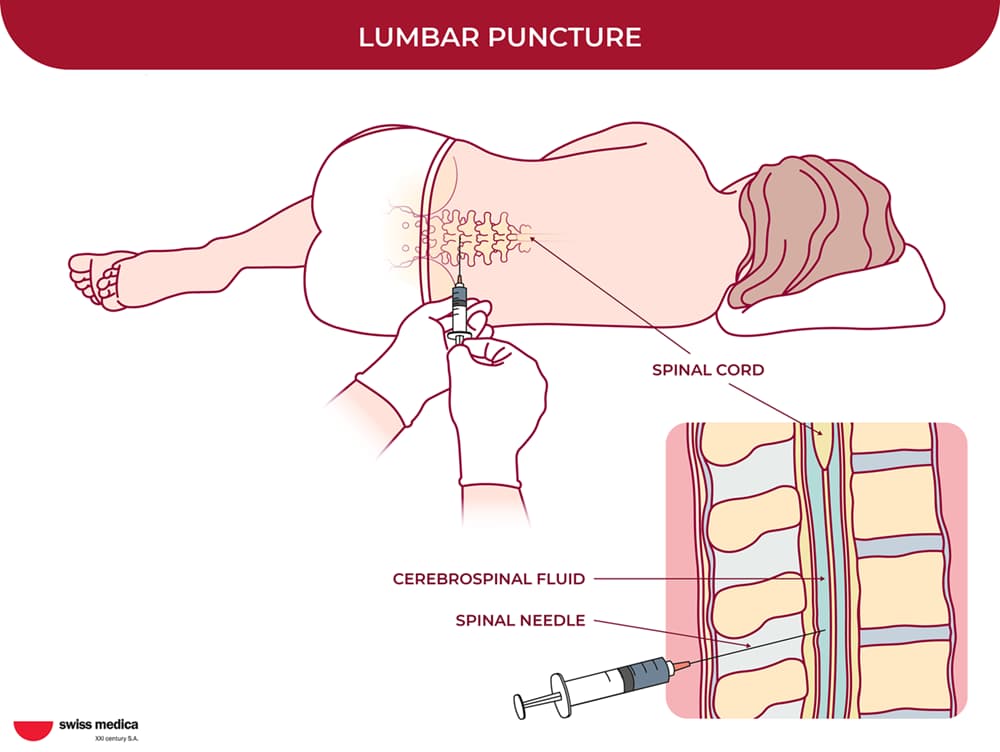
Cells are cultivated in Swiss Medica’s in-house laboratory. Depending on the case, stem cell transplants for dementia are administered by intravenous infusion or intrathecal (into the cerebrospinal fluid) injection.
Intravenous infusion and intrathecal injection, respectively—two gentle, doctor-guided procedures that help stem cells reach the brain and support regeneration without surgery.
Supportive therapies—such as secretome or exosome therapy—may be added to enhance regeneration.
Step 3—Rehabilitation and Long-Term Monitoring
After the stem cell injections for dementia, patients stay under observation in a comfortable hospital environment.
Post-treatment care includes physiotherapy, metabolic support, and remote follow-up.
Each program is fully supervised by our regenerative medicine specialists.
What to Expect After Therapy
Most patients notice gradual improvements within weeks or months. Commonly reported outcomes include:
- Better focus, memory, and verbal communication;
- Improved sleep and emotional stability;
- Reduced anxiety and confusion;
- Increased participation in everyday life.
While results differ, many patients experience their peak improvement around 3–6 months after therapy.
The effects of stem cell injections for dementia can last for several months, and progress made during this period tends to remain stable.
Real Patient Experiences
Sarah from Hawaii: Caring for Her Mother with Frontotemporal Dementia
Sarah from Hawaii came to Swiss Medica with her mother, who was diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia and given a five-year prognosis. After trying a short one-hour program in Mexico with limited benefit, she chose Swiss Medica in Serbia for a more comprehensive and medically supervised course, including physiotherapy, nutritional infusions, and intrathecal stem cell injections for dementia.
“At Swiss Medica everything was provided—the treatment, the care, the comfort,” she recalls. “In Mexico, we had to arrange everything ourselves.”
Her mother’s condition had been severe—minimal eye contact, anger, and total dependency. After therapy, Sarah noticed calmer behavior, better sleep, regular digestion, and a return of simple reactions. “There was life in her eyes again,” she says. “She could follow us, respond, and even say a few short words.”
She believes consistent rehabilitation at home—daily stretching, walking, and emotional support—helped maintain progress. “Don’t be so hard on yourself,” she advises other caregivers. “It gets better. Just don’t give up.”
Watch Sarah’s full interview on Swiss Medica YouTube channel.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Dementia
The mesenchymal stem cell therapy cost varies according to diagnosis, disease stage, and number of applications.
Typical programs for dementia range from €7,000 to €31,000* and include:
- Full medical evaluation and diagnostics;
- Stem cell cultivation and administration;
- Complementary therapies (secretome, IMR, exosomes);
- Accommodation, meals, and airport transfers;
- Follow-up consultations.
*Prices are indicative, based on January 2025, and may vary depending on the patient’s condition and required cell quantity.
Why Choose Swiss Medica for Stem Cell Therapy
Choosing where to receive stem cell therapy is an important decision—one that affects both safety and outcomes. At Swiss Medica, every aspect of the process is designed around transparency, quality, and patient comfort.
Experience and Expertise
Since 2011, Swiss Medica has treated over 10,000 patients from around the world. We focus on neurological and autoimmune conditions and offer stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s, and dementia.
Certified In-House Laboratory
All stem cell products are produced and tested in our EU GMP-grade lab, ensuring full control over safety and quality.
Patient-Centered Care
Our modern hospital in Belgrade, Serbia provides hotel-level comfort and 24/7 medical supervision. International patients receive full assistance with visas, transfers, and translators.
Affordable Pricing
Compared with Western Europe and the US, Swiss Medica offers world-class stem cell therapy to dementia patients at a more accessible cost thanks to lower operational expenses, making Serbia one of the best countries for stem cell therapy.
Getting Started with Consultation
Taking the first step toward healing can feel overwhelming—but we’re here to make it as smooth as possible.
Contact Us Today
Complete a short form, and our coordinator will schedule a free consultation about stem cell transplant for dementia with a regenerative medicine specialist on any convenient date.
Get Your Free Treatment Plan
Send your MRI, lab results, or diagnosis summary and receive a personalized plan with expected benefits, duration and cost of stem cell treatment for dementia estimate shortly after sending your reports.
FAQ
1. Is stem cell therapy a cure for dementia?
No, stem cell treatment for dementia may slow progression and improve quality of life but cannot fully reverse the disease.
2. Where can I get stem cell treatment for dementia?
Swiss Medica operates stem cell treatment for dementia in Belgrade, offering comprehensive programs for international patients.
3. What is the cost of stem cell treatment for dementia at Swiss Medica, and what factors influence it?
The cost of stem cell treatment for dementia varies depending on several factors—including the patient’s condition, disease stage, the number of cell applications, and the duration of stay in the clinic. Typically, ranges from €7,000 to €31,000*.
*Prices are indicative, based on January 2025, and may vary depending on the patient’s condition and required cell quantity.
4. Is the therapy safe for older patients?
Yes. MSC therapy is well tolerated by elderly patients under professional supervision.
List of References:
Zhang, X., Hou, X., Liu, T., Zhou, Z., Jiang, J., & Wu, X. (2024). Mesenchymal stem cells and exosomes improve cognitive function in the aging brain by promoting neurogenesis. Scientific Research Center, China–Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/aging-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2022.1010562/full
Livingston, Gill et al. The Lancet, Volume 404, Issue 10452, 572 – 628 Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2024 report of the Lancet standing Commission. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(24)01296-0/abstract
Regmi S., Liu D.D., Shen M., Kevadiya B.D., Ganguly A., Primavera R., Chetty S., Yarani R., Thakor A.S. Mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Strategies and limitations. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 2022;15:1011225. Department of Radiology, Interventional Radiology Innovation at Stanford (IRIS), Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2022.1011225
Uwishema, O., Ghezzawi, M., Wojtara, M. et al. Stem cell therapy use in patients with dementia: a systematic review. Int J Emerg Med 18, 95 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12245-025-00876-6
Bhatti J.S., Khullar N., Mishra J., Kaur S., Sehrawat A., Sharma E., Bhatti G.K., Selman A., Reddy P.H. Stem cells in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease – Promises and pitfalls. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2023.112264
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist