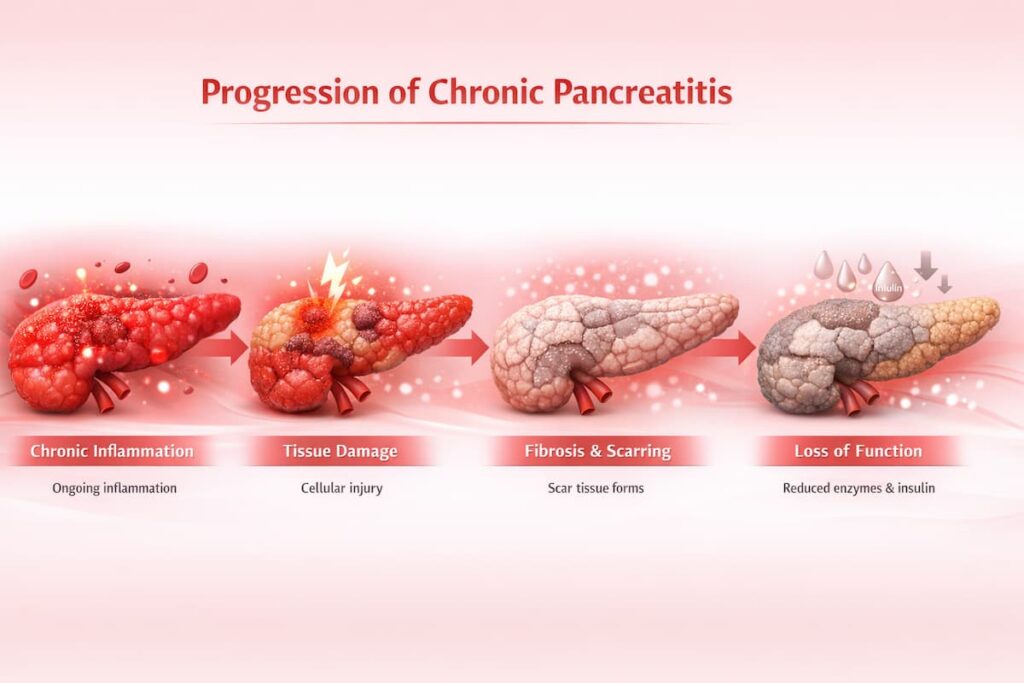
Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive inflammatory condition that causes ongoing damage to the pancreas. Over time, this leads to serious complications and dysfunctions impacting the digestive system and overall quality of life. Conventional treatments primarily focus on symptom management and do not halt disease progression.
In recent years, stem cell therapy for chronic pancreatitis has gained patients’ attention as a complementary approach that may help support the pancreas alongside conventional treatments. This new treatment for chronic pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal conditions aims to reduce inflammation, support tissue repair, and improve quality of life for patients. It does not cure pancreatitis or fully regenerate a severely damaged pancreas, but it can create an environment for better outcomes.
Understanding Chronic Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition in which the pancreas—an important organ that helps digest food and regulate blood sugar—becomes inflamed. Inflammation occurs due to abnormal activation of digestive enzymes inside the organ, resulting in damage to pancreatic tissue and surrounding structures.
Why the Pancreas Becomes Chronically Inflamed
In healthy digestion, pancreatic enzymes are produced in an inactive form and only become activated once they reach the intestines. Pancreatitis develops when these enzymes become activated while still inside the pancreas, causing the gland to “digest” itself and triggering inflammation of pancreatic tissue.
There are two main forms of pancreatitis:
- Acute pancreatitis is a sudden, potentially life-threatening inflammation of the pancreas. It can cause severe abdominal pain, systemic inflammation, and organ failure, requiring urgent medical care.
- Chronic pancreatitis develops over time when inflammation persists, gradually damaging the pancreas. Ongoing inflammation slowly damages the pancreas and leads to serious complications.
Progressive Tissue Damage and Loss of Pancreatic Function
As chronic pancreatitis progresses, the cumulative damage leads to a gradual loss of pancreatic function. Patients develop pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, meaning the pancreas no longer produces enough enzymes to properly digest food. At the same time, its ability to regulate blood sugar may decline, increasing the risk of diabetes.
Common Symptoms and Impact on Daily Life
Living with chronic pancreatitis often means dealing with ongoing symptoms and complications that affect comfort, nutrition, and energy:
| Chronic abdominal pain and flare-up patterns | Digestive complications and enzyme insufficiency | Weight loss, malnutrition, and fatigue |
| Persistent upper abdominal pain that may spread to the back | Poor digestion due to lack of digestive enzymes | Unintentional weight loss despite eating |
| Pain often worsens after meals | Bloating, gas, and oily or loose stools | Loss of muscle strength and endurance |
| Pain can disrupt sleep and daily activities | Need for pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy | Fatigue worsened by poor nutrition or diabetes |
What Causes Chronic Pancreatitis?
Main risk factors for chronic pancreatitis include:
- Alcohol-related pancreatic damage: Regular alcohol consumption can cause repeated inflammation in the pancreas, leading to long-term scarring.
- Genetic factors: Some people are born with gene changes that make the pancreas more vulnerable to inflammation, often leading to pancreatitis at a younger age.
- Metabolic factors: Very high blood triglyceride or calcium levels can repeatedly injure the pancreas if not controlled.
- Dietary factors: Chronic overeating, particularly diets high in fats, places additional stress on the pancreas and may contribute to recurrent inflammation, often alongside elevated triglyceride levels.
- Autoimmune conditions: In rare cases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the pancreas, causing inflammation that may respond to steroid treatment.
- Smoking independently increases the risk of chronic pancreatitis and worsens disease progression, especially when combined with alcohol or genetic risk.
- Idiopathic (unknown cause): In some patients, no clear cause is found despite testing. This can be frustrating, but timely treatment can help manage inflammation and preserve pancreatic function, regardless of the cause.
Conventional Treatments: Benefits and Limitations
Currently, there is no cure for chronic pancreatitis, so standard treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and maintaining quality of life rather than reversing existing damage.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain in chronic pancreatitis can be ongoing and challenging to manage. Treatment usually starts with non-opioid pain relievers and may progress to stronger medications if pain remains severe. Some patients also receive medications that target nerve-related pain.
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT)
When the pancreas no longer produces enough digestive enzymes, pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy may be recommended. Enzyme capsules taken with meals might help the body digest food, reduce diarrhea and bloating, and support weight maintenance. Most patients need to take enzymes long-term, and careful dosing is required to control symptoms.
Endoscopic and Surgical Interventions
Endoscopic treatments are used to relieve blocked ducts, drain fluid collections, or reduce pressure inside the pancreas, which may ease pain for some patients. Surgery is considered only when other treatments fail or when complications become severe.
Why These Approaches Cannot Help Structural Damage
Conventional treatments focus on relieving symptoms and managing complications. Once scarring forms in the pancreas, the damage cannot be reversed, although standard care may help slow further progression. For this reason, alternative pancreatitis treatments like stem cell therapy have been studied for the last decade—not as a cure, but as a potential way to reduce ongoing inflammation and support the pancreas’s remaining function.
Can Stem Cell Transplant Cure Pancreatitis?
Stem cell therapy is being studied as a potential new treatment for chronic pancreatitis, and clinical research is ongoing. However, at present, it cannot reverse severe pancreatic damage.
What it may offer is supportive help—easing ongoing inflammation and pain and creating better conditions for the pancreas to function. This approach is most suitable in earlier or moderate stages of the disease.
How Stem Cell Therapy for Chronic Pancreatitis Works
Stem cell treatment for pancreatitis most often uses mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which have a strong safety record. These adult stem cells can be obtained from sources like the placenta or umbilical cord after a healthy birth, as well as from bone marrow or adipose tissue. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy is valued for its ability to support the body’s own repair processes and help regulate inflammation.
Reducing Chronic Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation
In autoimmune chronic pancreatitis, persistent immune activation damages pancreatic tissue, and stem cell therapy for chronic pancreatitis with MSCs may help regulate this response and reduce inflammation. In other forms, their potential benefits are limited to tissue support, repair processes, and reduction of secondary inflammation, without reversing established damage.
Supporting Tissue Repair and Microcirculation
MSCs release growth factors and anti-apoptotic (cell-saving) molecules that support tissue repair. They can also improve local blood flow, allowing remaining pancreatic cells to receive more oxygen and nutrients. While this does not reverse scarring, it may help slow progression and support remaining function.
Potential Effects on Pain Signaling and Digestive Function
Over time, stem cell therapy for pancreatitis may help reduce pain sensitivity by lowering pressure and inflammation around pancreatic nerves. Supporting the pancreatic environment may also help preserve remaining digestive function, which can improve comfort, appetite, and response to enzyme therapy in some patients.
Learn more about how MSCs work at the cellular level. In our article, we explain the mechanisms of stem cells as alternative pancreatitis treatments in a clear and scientifically grounded way.
Read moreSafety of Stem Cell Therapy for Pancreatitis and Clinical Evidence: What Science Says
Current research and clinical experience suggest that MSC therapy as an alternative pancreatitis treatment is generally well tolerated and effective.
- Early pancreatitis studies are reassuring. Initial human reports and pilot studies in chronic pancreatitis show good tolerability, with some patients reporting symptom improvement.
- Mild and temporary side effects. Reported reactions are usually short-lived and may include low-grade fever, fatigue, or headache after infusion.
- No evidence of cancer risk. Long-term studies have not shown an increased risk of tumors or abnormal tissue growth after MSC therapy.
Expected Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Pancreatitis
Results can vary between individuals and are also influenced by treatment protocols and the quality of the stem cells used. At Swiss Medica, a stem cell clinic in Serbia, we see a range of responses in patients with chronic conditions, including pancreatitis.
| Stem cells aid in chronic pain relief and decrease frequency | Lower daily pain, fewer or milder flare-ups, and, in some cases reduced need for pain medication |
| Improved digestion and nutrient absorption | Less bloating and oily stools, better tolerance of meals, weight stabilization, improved response to enzyme therapy |
| Support of remaining pancreatic function | Possible slowing of further loss of enzyme or insulin production, greater functional stability over time |
| Better overall quality of life | Improved energy, better sleep, reduced fatigue, and improved emotional well-being |
Contact us
To better understand what stem cell therapy for pancreatitis may offer in your case, you can consult the medical team at Swiss Medica. A free, no-obligation consultation includes a review of your medical history and an assessment of your suitability for treatment.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
— A patient from Ireland
“Before the treatment, my digestion was difficult—constant stomach pain, frequent trips to the toilet, blood in the stool, and total exhaustion. Now my stool has already improved, my inflammation levels are close to normal, and I feel much more energy. After years of flare-ups, it feels like my digestion is finally starting to settle.”
You can find more reviews on our YouTube channel.
Possible Side Effects and Risk Management in Chronic Pancreatitis
At Swiss Medica, the majority of our patients tolerate stem cell treatments for pancreatitis well:
- Side effects are usually mild and temporary, like brief fatigue or a low-grade fever after infusion.
- Safety is closely managed, with medical screening and continuous monitoring before, during, and after treatment. Special attention is given to our GMP-certified laboratory, where stem cells are produced under strict conditions to ensure quality, sterility, and viability.
Learn more about our laboratory to see how stem cells and their derivatives are produced, what equipment is used, and how these processes can influence patient outcomes.
Read moreSwiss Medica’s Stem Cell Treatment Program for Pancreatitis
Swiss Medica offers a structured stem cell treatment for chronic pancreatitis focused on safety, personalization, and continuity of care.
Diagnostic Assessment and Eligibility Review
Treatment begins with a free online consultation and careful review of your medical history, imaging (CT or MRI), lab tests, and current symptoms. Doctors assess disease stage, overall health, and pancreatic function to determine whether stem cell treatment for pancreatitis is appropriate. Not every patient is accepted—this step helps ensure the treatment is both safe and potentially beneficial.
Cell Preparation and Administration
Stem cells are prepared in Swiss Medica’s in-house laboratory. Depending on your case, doctors may use your own cells (from adipose tissue or bone marrow) or donor cells from screened umbilical cord tissue.
In some cases, doctors may advise combining physiotherapy, nutritional supplements, and cell-based products such as exosomes or secretomes to deliver faster signaling molecules and support the activity of MSCs. Each option follows strict quality and safety controls.
For pancreatitis, stem cell therapy is typically delivered through an intravenous infusion with continuous medical monitoring. Some patients may receive more than one stem cell injection, depending on their individualized treatment plan.
Supportive Therapies and Monitoring
Alongside stem cell therapy, Swiss Medica may include supportive treatments such as nutritional support, physiotherapy, antioxidant infusions, or oxygen therapy, depending on individual needs. Medical staff monitor vital signs daily and track symptoms and lab markers throughout the stay. Patients remain under observation after treatment and receive clear post-care instructions and follow-up planning before returning home.
Timeline of Stem Cell Treatment for Pancreatitis: When Patients See Results
Improvements usually appear gradually. At Swiss Medica, many patients first notice better energy and overall well-being within weeks, followed by reduced pain over 1–3 months. In some cases, patients experience improvements in digestion or weight stability over a period of 3–6 months. Experiences vary, but changes are typically progressive rather than immediate.
Who May Benefit From Stem Cell Therapy for Pancreatitis
Not every patient with chronic pancreatitis is a candidate for stem cell therapy. At Swiss Medica, we consider several factors to determine who may benefit the most:
| Category | Suitable Candidates | May Not Be Eligible |
| Pancreatitis status | Stable chronic pancreatitis, no active flare | Acute pancreatitis, active infection, or sepsis |
| Symptoms & response to care | Persistent pain or digestive issues despite standard therapy | |
| Pancreatic function | Early to moderate loss with remaining function | End-stage pancreatic failure with minimal function |
| Overall health | Stable heart, liver, kidneys; no major instability | Severe uncontrolled comorbidities or frailty |
| Cancer & safety factors | No current or suspected malignancy | Active cancer |
| Lifestyle & readiness | Alcohol abstinence, smoking cessation, able to follow care plan |
How Do Stem Cell Therapy Costs Compare in the United States, Europe, and Serbia?
Stem cell therapy cost varies widely by country: in the USA it is mostly limited to clinical trials or expensive private clinics, while in Europe high regulatory and facility costs make treatment costly.
Many patients therefore look for the cheapest country for stem cell treatment, often in Latin America or Asia, but lower prices may mean weaker regulation. Serbia, particularly Swiss Medica, offers a safer balance—medically supervised regenerative treatment for the pancreas at more accessible prices.
| Region | Typical Cost |
| United States | $15,000–$30,000+ |
| Europe | €10,000–€40,000 |
| Serbia (Swiss Medica) | €7,000–€31,000* |
*Prices are indicative and based on 2026 estimates; they may vary depending on condition severity and required cell quantity.
Why Patients Choose Swiss Medica
We combine expertise, safety, and a patient-centered environment, which is why many patients choose us:
- Proven experience—14 years in regenerative medicine, treating over 10,000 patients for chronic conditions in neurology, gastroenterology, and endocrinology.
- Personalized protocols—treatment plans tailored to disease stage, symptoms, and patient goals, not a one-size-fits-all approach.
- In-house GMP laboratory—full control over stem cell quality, safety, and consistency, produced under European standards.
- Multidisciplinary care—a coordinated team of doctors and rehabilitation professionals.
- International patient support—a newly built, fully equipped hospital with comfortable accommodations, airport transfers, translation, and nutritional meals are provided to make patients feel at home.
- Transparent approach—realistic expectations and clear communication at every step.
How to Start Your Treatment Journey
Starting your treatment journey begins with a clear, supportive conversation about your health and goals. Our medical team reviews your case carefully and helps you understand whether stem cell treatment for chronic pancreatitis may be a suitable option for you.
Get a free online consultation
Book a free, no-obligation consultation with Swiss Medica to discuss your condition in detail and explore your possible next steps with our medical team.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long do results last?
Results vary by individual. Stem cells for pancreatitis may remain active for several months up to 1–2 years, and many patients report reduced pain and improved pancreatic function during this time.
2. Can stem cell therapy for pancreatitis replace enzyme therapy or pain medication?
No, not immediately. Stem cell therapy works alongside standard care. Over time, some patients may need lower doses of pain medication or enzymes, but any changes must be guided by a doctor.
3. Can I bring a caregiver?
Yes. Swiss Medica welcomes companions. Rooms can accommodate one caregiver, who may stay with you throughout treatment and attend consultations if you wish.
List of References:
Wang, Y., Yi, H. & Song, Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 12, 545 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x
Petrov M. S., Shanbhag S., Chakraborty M., Phillips A. R. J., and Windsor J. A., Organ failure and infection of pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis, Gastroenterology. (2010) 139, no. 3, 813–820, https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.010
Kawakubo K, Ohnishi S, Kuwatani M, Sakamoto N. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute and chronic pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jan;53(1):1-5. doi.org/10.1007/s00535-017-1363-9
Xuan, X., Tian, C., Zhao, M. et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in cancer progression and anticancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Cell Int 21, 595 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02300-4
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist