Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases is no longer just a futuristic idea—it’s already remodeling the way we approach treatment and recovery. The fundamental difference from traditional medicine lies in this therapy’s ability to promote healing at the cellular level and to activate the body’s natural repair systems, which ultimately leads to long-term health rather than addressing a single issue.
Whether you’re dealing with a chronic condition, searching to avoid or postpone surgery, or just starting to explore your options to support healthy aging, one question comes up: what diseases can be cured with stem cells?
In this article, we’ll walk you through the list of diseases treated by stem cells, how the therapy works and answer some of the most common questions people have about this innovative field: how do stem cells really help and support your body? Can this method heal some conditions? How long does the effect last? If you’re wondering whether stem cells could be the answer you’ve been looking for—keep reading.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases isn’t just a simple injection or a magic pill but rather a part of regenerative medicine and includes a number of steps that help the body heal itself. It works on a variety of levels, including cell repair and immune system regulation. It involves the use of stem cells—either from the patient’s own body (autologous) or from a donor (allogeneic)—to target inflammation, tissue degeneration, or immune dysfunction.
Stem cell therapy is often combined with traditional treatments to improve outcomes and support long-term recovery. As a result, the list of diseases treated with stem cells continues to grow, covering a wide range of chronic and degenerative conditions.
What Are Stem Cells?
In simple terms, stem cells are the “blank cells” in your body that have the ability to turn into many different types of specialized cells, like those that build bones, nerves, and muscles. They play a key role in tissue growth and regeneration throughout life.
There are several types of stem cells used in medical research and therapy:
- Adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs):
These cells come from tissues like bone marrow, fat, and the umbilical cord and have the inherent potential to differentiate into cell types such as bone, cartilage, or fat cells. However, they don’t automatically turn into those cells in the body or in clinical use. Differentiation usually requires directed differentiation in the lab, under controlled conditions with the right growth factors. - Embryonic stem cells:
Derived from early-stage embryos, these cells can become any cell type in the body. However, their use raises ethical concerns and carries a higher risk of uncontrolled growth. - Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs):
These are adult cells genetically reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells. They are promising for research, but not yet widely used in clinical settings. - Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs):
These are blood-forming stem cells typically used in bone marrow transplants for conditions like leukemia and other blood disorders.
We only use adult mesenchymal stem cells at Swiss Medica. These cells do not come from embryos. The difference is important for both moral and safety reasons. The MSCs we use are:
- Ethically sourced from umbilical cord and placental tissues, with no involvement of embryonic cells.
- Clinically safe, with no risk of tumor formation.
- Well-tolerated, with only mild, short-term side effects such as slight fatigue or low-grade fever.
- Stable over time, showing no adverse long-term effects.
Depending on the condition that can be treated with stem cells, we also use autologous MSCs, which are derived from the patient’s own bone marrow or fat tissue.
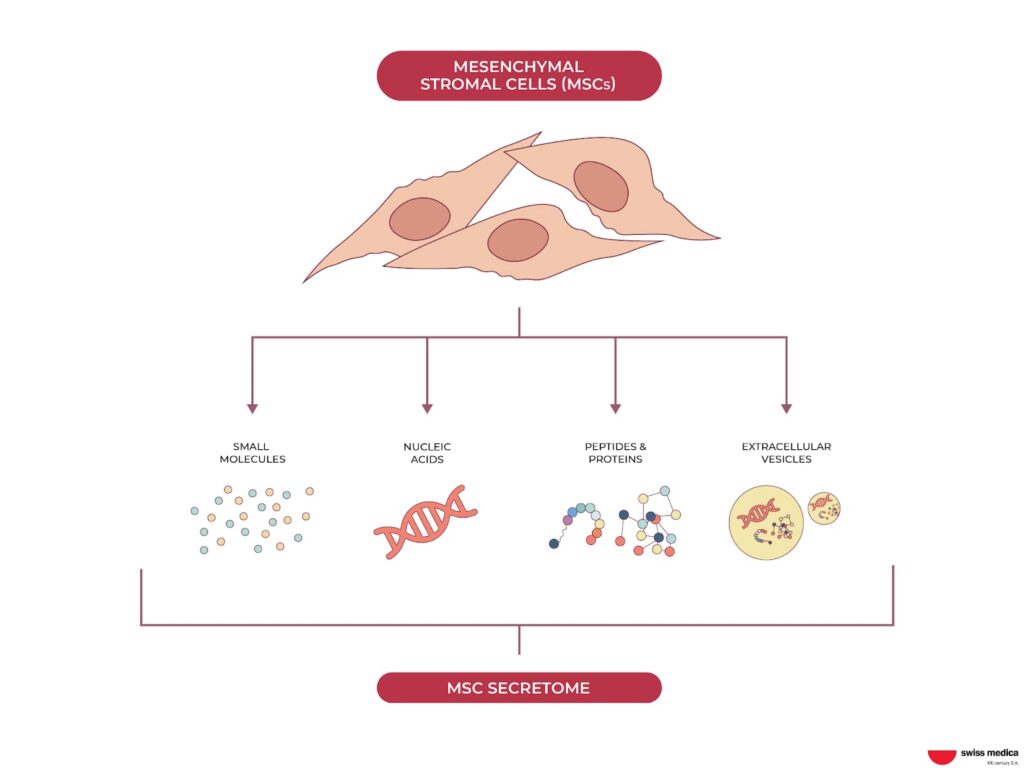
How Do Stem Cells Work in the Body?
Stem cell treatment for diseases such as autism, multiple sclerosis, or heart problems may support the body’s natural repair processes by lowering inflammation, regulating the immune system, and encouraging tissue regeneration. Here are the key ways stem cells help your body:
- Secretion of biologically active substances
Stem cells release growth factors and other signaling molecules that reduce inflammation and trigger tissue regeneration. - Improved circulation and collagen production
These growth factors enhance blood flow, stimulate collagen synthesis, and accelerate healing—supporting both internal recovery and external rejuvenation. - Exosome and microvesicle activity
Stem cells release exosomes and microvesicles—tiny messengers that deliver proteins to damaged cells, promoting repair and cellular communication. - Immune system regulation
MSCs help restore immune balance by reducing chronic and autoimmune inflammation, supporting a more regulated immune response. This is especially useful in autoimmune or chronic inflammatory conditions. - Formation of new blood vessels
Stem cells support angiogenesis—the development of new blood vessels—which improves oxygen and nutrient delivery to tissues and speeds recovery.
These mechanisms help us understand how various diseases are treated by stem cells and why stem cell therapy is gaining popularity and recognition, ranging from joint and neurological disorders to cosmetic rejuvenation and recovery after an injury.
Get a free online consultation
If you have questions about MSCs or want to better understand how stem cell therapy may apply to your case, our medical advisors are here to help.
Fill out the form below to ask your question.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
What Are 5 Possible Uses of Stem Cells?
There are many medical conditions that can be treated with stem cells, but each case is different.
Regeneration of Damaged Tissue
Stem cells support the repair of bones, nerves, cartilage, and skin. This makes them valuable for treating joint problems, soft tissue injuries, and wounds after surgery.
Immune System Modulation
One of the main benefits of stem cell therapy is that it can control overactive immune responses. This helps control autoimmune diseases and lower the number of relapses in diseases like lupus and multiple sclerosis.
Blood and Bone Marrow Disorders
Some of the conditions that can be treated with stem cells include leukemia, lymphoma, and various types of anemia, where stem cell transplants are already part of standard care.
Treatment of Neurological Damage
Stem cells are being explored as a treatment for spinal cord injuries, strokes, and neurodegenerative diseases by promoting nerve regeneration and reducing inflammation in the brain.
Cosmetic and Anti-Aging Applications
What diseases can mesenchymal stem cells treat beyond traditional medicine? One emerging area is stem cell therapy for anti-aging. This includes skin rejuvenation, wrinkle reduction, and exosome-based treatments that enhance skin tone and elasticity.
Common Diseases Treated by Stem Cells
The benefits of stem cell therapy extend across a wide spectrum of health conditions. This list of diseases treated by stem cells shows how regenerative medicine can provide meaningful support and relief.
Neurological Disorders Treated by Stem Cells
Stem cell therapy is becoming more common for neurological disorders due to its ability to protect nerve cells, lower inflammation, and improve neuroplasticity. It can help with recovery and managing symptoms for:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Stroke Recovery
- Cerebral Palsy
Better motor function, less muscle stiffness, and better daily functioning are some of the improvements that may happen. Here’s what some of our MS patients had to say after stem cell injections for MS:
Autoimmune Conditions and Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells can help normalize immune responses, making them effective for various autoimmune disorders. They work by calming down an overactive immune system and helping it stay in balance. Conditions that may benefit include:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Lupus (SLE)
- Crohn’s Disease
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Patients often report fewer relapses, improved lab markers, and a reduced need for immunosuppressants.
Autism
Patients with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) have different behavioral and neurological challenges. These can include difficulties with communication and social interaction, hyperactivity, poor sleep, and self-stimulatory behaviors.
ASD is also included in the list of diseases treated by stem cells. At the core of this approach are MSCs, which show promise due to their ability to:
- Calm the immune system, especially when inflammation or immune dysregulation plays a role.
- Reduce oxidative stress, helping to create a more stable internal environment for brain function.
- Enhance neural connectivity, potentially supporting better cognitive development and communication.
While there’s currently no stem cell cure for autism, early clinical studies indicate that MSC therapy may help reduce both core and associated symptoms of autism. As a result, more families are exploring stem cell therapy as part of a broader, personalized care strategy for children on the spectrum.
Cardiovascular Conditions
Stem cell therapy is gaining attention in cardiology for its ability to repair damaged tissue, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation. It’s most commonly used for:
- Heart failure
- Ischemic heart disease
- Peripheral artery disease
- Stroke recovery
For example, stem cell treatment for heart failure supports cardiac regeneration, stimulates new blood vessel growth (angiogenesis), and helps regulate inflammation. As a result, patients may experience better heart function, increased stamina, and fewer hospital visits.
Metabolic & Endocrine Diseases
Stem cell treatment for endocrine and metabolic diseases aims to reduce chronic inflammation, restore hormonal balance, and promote tissue regeneration. This approach is showing promise in managing conditions such as:
- Type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Metabolic syndrome
While type 2 diabetes and other metabolic conditions are not yet among the diseases cured by stem cells, stem cell therapy—particularly with MSCs and bone marrow-derived cells—shows potential to improve glucose regulation and reduce complications.
Benefits may include better glucose control, improved insulin sensitivity, and enhanced overall health.
Orthopedic & Joint Problems
Stem cells are widely used in treating conditions like osteoarthritis, tendinitis, and sports-related injuries. By reducing inflammation and encouraging cartilage regeneration, they help restore joint function and ease pain.
At Swiss Medica, patients have been able to avoid or postpone invasive procedures like knee or hip replacements by choosing stem cell treatment as a less disruptive alternative. While not a guaranteed solution, many of our patients have experienced meaningful improvements following stem cells knee therapy:
Arthritis and other musculoskeletal conditions are frequently treated with regenerative approaches. While outcomes vary, some patients experience the following results:
- Decreased joint inflammation
- Improved range of motion
- Reduced need for surgery
Stem Cell Therapy Benefits and Risks
For those exploring stem cell therapy, understanding both the benefits and limitations is crucial for making informed decisions.
Key Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy
| Key Advantages | How It Works |
| Personalized and minimally invasive | Treatments are tailored to the patient’s condition and involve no-pain procedures. |
| Promotes tissue regeneration | Effective for the health issues where damaged tissues must be restored, from arthritis to heart attacks and multiple sclerosis. |
| May delay or avoid surgery | Offers an alternative to invasive procedures such as joint replacements. |
| Reduces pain and inflammation | Provides relief in conditions like arthritis, injury recovery, and autoimmune diseases. |
| Helps manage complex diseases | In neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s), it may slow progression and improve function. |
| Stem cell treatments for chronic diseases are improving patient outcomes | There are successful applications in orthopedic, neurological, and metabolic disorders. |
Is Stem Cell Therapy Safe?
When it comes to stem cell therapy risks and success, one of the most important factors is the quality of the cells and procedures. Treatments should always be conducted in sterile, GMP-certified facilities to ensure safety and effectiveness.
When administered in such settings, MSC therapy is considered safe. Unlike pluripotent cells, MSCs are multipotent—they can only differentiate into specific tissue types and do not carry a risk of uncontrolled growth or tumor formation.
Potential Risks You Should Know About
Some patients may experience mild, short-term reaction—but these typically resolve on their own. Still, it’s important to understand the potential risks of stem cell therapy, so let’s take a closer look.
| Possible Side Effect | Description | Severity |
| Soreness | Localized pain or discomfort at the injection site | Mild |
| Swelling | Mild inflammation or puffiness around the injection area | Mild |
| Low-grade fever | Slight rise in body temperature following treatment | Mild |
| Headache | General discomfort or pressure in the head | Mild |
Stem Cell Therapy Success Rate
Which type of disease might most likely be cured by stem cell transplantation?
Stem cell therapy success rates vary by condition and individual factors, but patient outcomes report improvements in 60–80% of cases, especially in MS, arthritis, and autism. However, stem cell therapy is not a guaranteed cure and requires proper evaluation.
How Expensive Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell injection costs vary by country and clinic. In the U.S., prices can range from $5,000 to more than $50,000. More affordable, yet high-quality treatment options are available in accessible locations, such as Mexico and Serbia.
At Swiss Medica, we offer stem cell therapy as a comprehensive package tailored to each patient. Prices usually range from €7,000 to €31,000*, depending on the patient’s condition and the treatment plan.
*The prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
Where Do Celebrities Get Stem Cell Treatments?
Many celebrities turn to stem cell-based therapy at international clinics known for cutting-edge care and privacy. Countries like Panama, Germany, Switzerland, and Serbia are top destinations.
Clinics such as Swiss Medica are especially popular for combining medical innovation, GMP-certified procedures, and discreet, personalized care. For public figures and high-profile clients, Swiss Medica offers a dedicated VIP program—with full medical privacy, exclusive accommodations, and tailor-made treatment plans.
Is There Stem Cell Therapy in the USA? Is It Legal?
Stem cell treatments in the USA are legal but heavily regulated. However, only a limited number of diseases treated by stem cells are FDA-approved. These are mostly blood-related cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
Other uses, especially for autoimmune, neurological, and orthopedic conditions, are still being studied and are usually only available through clinical trials or at specialized clinics outside the U.S.
How to Choose a Reliable Stem Cell Clinic
The success of your stem cell therapy depends a lot on the clinic you choose. Before making a decision, think about the following:
- Check the clinic’s reputation
Check out success stories, and reviews from those who have received treatment there. Reputable clinics are open about their results and often treat more than one condition. - Speak with qualified professionals
Make an appointment with a specialist that has proven experience with stem cell therapies. The clinic should look at your case carefully instead of giving you a one-size-fits-all answer. - Ask the right questions.
Before committing, make sure you understand:
- Whether stem cell therapy is suitable for your specific condition
- What the treatment includes, step-by-step
- How safety and quality are maintained
- The full cost and any additional fees
- What kind of aftercare is available once you return home
A reputable clinic will take the time to answer your questions without pressure or exaggerated promises, will never claim that all diseases are cured by stem cells, and will support you through each stage of treatment.
What Makes Swiss Medica a Trusted Choice for Stem Cell Treatment?
At Swiss Medica, a regenerative medicine clinic in Belgrade, Serbia, we take a comprehensive, patient-centered approach to regenerative therapy. It is a popular place for people looking for new, scientifically proven stem cell treatments. Here’s why:
Cutting-Edge Facilities & Technology
Our medical center features modern infrastructure and a fully equipped in-house lab. This allows us to produce over 31 types of advanced biomedical products—including mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes, PRP, and M2 macrophages—under strict quality control and in line with European health standards. Every stage of treatment, from cell sourcing to application, happens under one roof.
Experienced Specialists in Regenerative Medicine
Our multidisciplinary team has been working in the field for more than 13 years and combines scientific knowledge with clinical care. We constantly improve our treatments through research, using only safe, clinically approved methods that are tailored to each patient’s health needs.
Global Care for International Patients
Located within easy reach of major European hubs, we welcome patients from across the world. Our dedicated coordinators assist with travel logistics, accommodation, and interpretation—ensuring a smooth experience before, during, and after therapy.
With over 10,000 successful cases, Swiss Medica is recognized for delivering reliable, personalized stem cell treatments in a professional and supportive environment.
Our new hospital in Belgrade provides a patient-centered environment for advanced stem cell therapy for various conditions.
Contact us
How can stem cells be used to treat diseases and injuries? Talk to a Swiss Medica medical advisor today—we’re here to help you understand whether stem cell therapy could be the right path for you.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common conditions treated with stem cell therapy?
To help you navigate the list of diseases treated with stem cells, we’ve highlighted some of the most frequently treated conditions below.
- Osteoarthritis and joint injuries
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Parkinson’s disease
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis
- Spinal cord and nerve damage
These fall under the broader list of diseases treated by stem cells, which continues to grow with ongoing research.
2. What diseases require a stem cell transplant?
Strictly speaking, most diseases do not require a stem cell transplant as the only option. However, stem cell transplants are an established part of treatment for some blood-related cancers, like leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. In some cases, like autoimmune, neurological, or degenerative diseases, stem cell therapy may be a good addition to a larger treatment plan.
3. Can stem cells cure diseases?
No, stem cells do not offer a guaranteed cure, and there are no diseases cured by stem cells. However, they can significantly improve symptoms, slow disease progression, and support tissue repair in many chronic and degenerative conditions. Their effectiveness depends on the specific disease, the stage, and the individual response to treatment.
4. How long does the treatment take?
The procedure is relatively quick and minimally invasive. The stem cell injection usually takes between one and two hours, depending on how the stem cells are given and what medical issue is being treated.
5. How many sessions are needed?
The number of sessions depends on the patient’s health status and the disease being treated. Some individuals see results after just one session—especially in targeted treatments like joint repair. For people with chronic or systemic conditions, like autoimmune or neurological diseases, it may be recommended to have more than one session over time. Each plan is customized to your body’s response.
6. Is the procedure painful?
Most patients feel very little or no pain, like getting a blood test. Some people may have minor side effects like temporary swelling or mild pain at the injection site, but these usually go away on their own without the need for medication.
List of References:
Kvistad Christopher Elnan , Kråkenes Torbjørn , Gjerde Cecilie , Mustafa Kamal , Rekand Tiina , Bø Lars. Safety and Clinical Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment in Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury, Multiple Sclerosis and Ischemic Stroke – A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Frontiers in Neurology, Volume 13 – 2022. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/neurology/articles/10.3389/fneur.2022.891514
Jasim, S.A., Yumashev, A.V., Abdelbasset, W.K. et al. Shining the light on clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther 13, 101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02782-7
Tamouza Ryad , Volt Fernanda , Richard Jean-Romain , Wu Ching-Lien , Bouassida Jihène , Boukouaci Wahid , Lansiaux Pauline , Cappelli Barbara , Scigliuolo Graziana Maria , Rafii Hanadi , Kenzey Chantal , Mezouad Esma , Naamoune Soumia , Chami Leila , Lejuste Florian , Farge Dominique , Gluckman Eliane. Possible Effect of the use of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Review. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. Volume 10 – 2022. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cell-and-developmental-biology/articles/10.3389/fcell.2022.809686.DOI=10.3389/fcell.2022.809686
Panos LD, Bargiotas P, Arnold M, Hadjigeorgiou G , Panos GD. Revolutionizing Stroke Recovery: Unveiling the Promise of Stem Cell Therapy. Published 29 March 2024 Volume 2024:18 Pages 991—1006, https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S460998
Gadelkarim M, Abd Elmegeed A, Allam AH, Awad AK, Shehata MA, AbouEl-Enein A, Alsadek ME, Abo Deeb M, Afifi AM. Safety and efficacy of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine. 2022 Oct;89(5):105404. doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2022.105404
Li L, Hui H, Jia X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Xu Q, Zhu D. Infusion with Human Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves β-cell Function in Patients and Non-obese Mice with Severe Diabetes. Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 1;6:37894. doi.org/10.1038/srep37894
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist