Type 2 diabetes remains a major health challenge worldwide, affecting hundreds of millions of people and rising every year. Conventional treatments manage blood glucose, but over time they may require more intensive control to maintain the same effect.
Scientists have been exploring stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes as a complementary approach that may help support insulin production and improve the body’s glucose control. Early evidence shows that patients treated with stem cells for type 2 diabetes have a tendency to improve insulin levels and reduce their need for medication.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes and Its Challenges
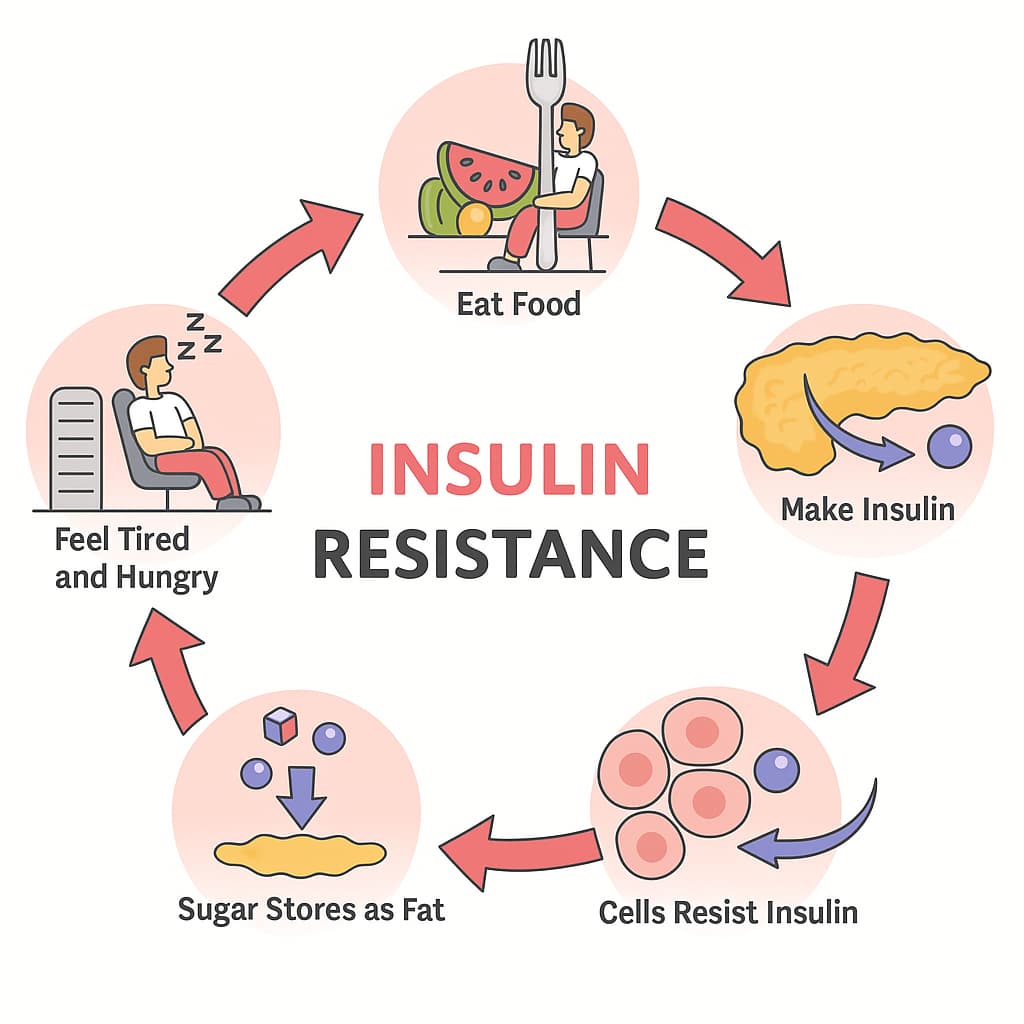
Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) develops when the body’s cells become resistant to insulin and the pancreatic beta cells can no longer sustain the high level of insulin production needed to keep blood sugar normal. As a result, glucose builds up in the blood (hyperglycemia), gradually damaging organs. Unlike type 1 diabetes, T2DM develops slowly and is linked to excess weight and inactivity.
Treatment usually involves diet changes, exercise, oral drugs, and sometimes insulin injections. Medications help control blood sugar and can slow the decline of beta-cell function.
Stem cell treatment for type 2 diabetes is being explored as a way to support insulin-producing cells and reduce inflammation, aiming to influence the underlying disease mechanisms rather than just the symptoms. In addition to traditional treatments, it may result in better patient outcomes.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes?
In the case of type 2 diabetes, stem cell treatment harnesses the body’s own regenerative abilities to support the pancreas and other affected tissues, resulting in improved blood sugar control.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Treatment
Several types of stem cells for type 2 diabetes have been studied for treating the disease, but mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are the most widely used and scientifically supported in clinical trials. MSCs can be derived from various sources:
- Autologous: Collected from the patient’s own body, usually from bone marrow or fat, sometimes from blood or dental tissue.
- Allogeneic: In some cases, donor stem cells are used, like those from umbilical cord or placental tissue collected safely after birth with consent.
How Stem Cells Work in Diabetes Management
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in type 2 diabetes works mainly through anti-inflammatory and metabolic effects. It may reduce insulin resistance, protect existing insulin-producing β-cells, and help the remaining cells function more effectively. Additionally, MSCs can improve blood flow and lipid metabolism.
As a result, patients may see a 1% drop in HbA1c (the three-month average blood sugar) and require less diabetes medication.
Are you curious about how stem cells work in type 2 diabetes? Our article will explain how MSCs release growth factors and support natural regeneration.
Learn moreDive into the Details: How Stem Cell Therapy Helps the Body Heal
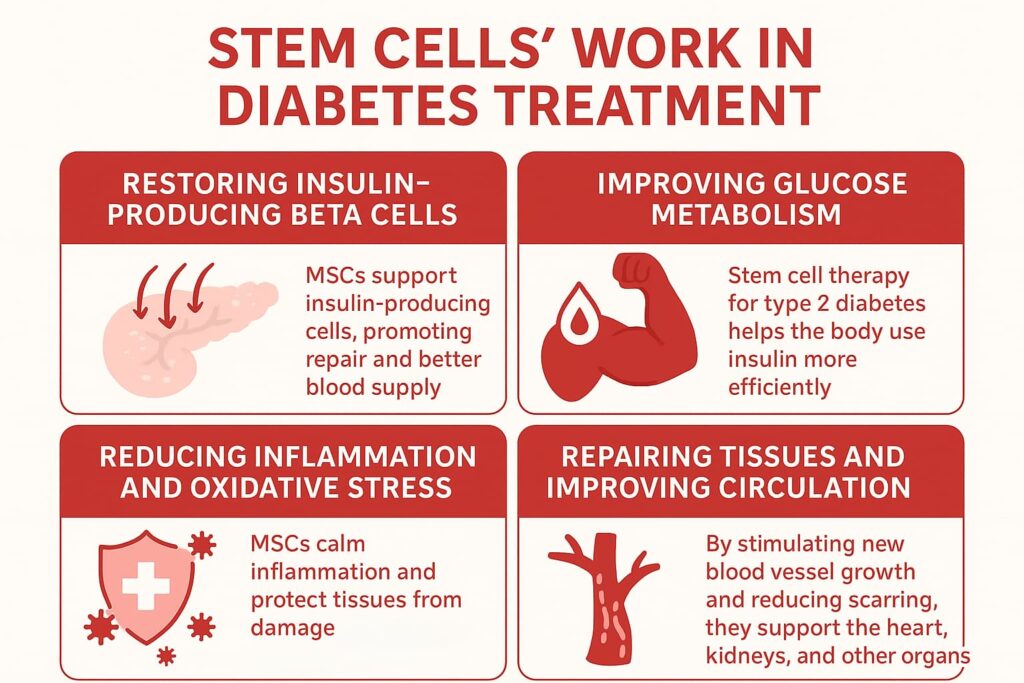
Here are the key ways stem cell treatment for type 2 diabetes helps the body recover:
- Potential support for insulin-producing β-cells: MSCs may help the existing cells function better by reducing inflammation, promoting cellular repair, and improving blood supply in the pancreas.
- Improving glucose metabolism: Stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes has the potential to help the body use insulin more efficiently. MSCs release cytokines that improve insulin response in muscles, the liver, and fat, thereby stabilizing blood sugar.
- Reducing inflammation and oxidative stress: MSCs calm inflammation and protect tissues from damage, slowing the progression of complications.
- Repairing tissues and improving circulation: By stimulating new blood vessel growth and reducing scarring, MSCs support the heart, kidneys, and other organs.
MSC-derived exosomes—tiny particles that carry the same healing signals—may enhance these effects by assisting the body’s natural insulin production.
Scientific Background and Clinical Evidence
Stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes has moved from idea to reality through numerous studies and clinical trials in the past decade:
- Preserved insulin production: In one placebo-controlled trial, 82% of patients treated with their own bone marrow stem cells cut insulin use, showing improved pancreatic insulin production.
- Better glucose control: A meta-analysis of 13 trials showed lower HbA1c and insulin requirements a year after treatment, with higher fasting C-peptide levels (a marker of insulin production) and improved post-meal glucose control.
- Safety profile: These trials report that stem cell therapy is well tolerated, with no serious treatment-related side effects.
Clinical Outcomes and Success Rates
Most patients see measurable improvements after stem cell treatment for type 2 diabetes—but individual results vary. Here’s a summary of outcomes and success rates:
| Aspect | What Studies Show | What Patients Can Realistically Expect |
| Insulin Production | Insulin needs have been reduced in 82% of cases, and C-peptide levels have risen, indicating that pancreatic activity has been restored. | Possible reduction in insulin or medication use; improved body’s own insulin production, but not full independence from treatment. |
| Glucose Control | HbA1c drops by 0.5–1%, and insulin needs decrease by about 14 units/day on average. | Better blood sugar stability over several months; less medication required. |
Many patients ask, “Can stem cells cure type 2 diabetes?” The answer is no, but therapy with stem cells for type 2 diabetes can improve control and outcomes. The outcomes vary depending on age, disease stage, and post-treatment lifestyle. Starting treatment earlier and maintaining a healthy lifestyle after treatment will result in better outcomes.
At Swiss Medica in Belgrade, the stem cell therapy success rate is high. In 80% of patients, we see a positive effect, which may include lower blood sugar levels, reduced need for medication, or fewer complications.
How Long Do the Effects Last?
Improvements usually last for about 3–6 months after one treatment, and some patients may experience better insulin production and lower insulin needs for up to two years.
Lifestyle and follow-up care make a big difference in the longevity of results. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and follow-up care help preserve the results.
Who Can Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
Stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes is not a one-size-fits-all solution that may not be appropriate for all patients. Main criteria usually include the following:
| Eligibility Criteria | Description |
| Age and Diagnosis | Adults aged 30–75 with confirmed type 2 diabetes. |
| Insulin Production | Some remaining pancreatic function with adequate C-peptide levels. |
| Diabetes Control | Suitable for patients whose diabetes is not well controlled despite medication, insulin, and lifestyle measures. |
| Health Condition | Must be in stable condition without acute complications. |
| Exclusion Criteria | Stem cell treatment for type 2 diabetes is not suitable for patients with type 1 diabetes, active cancer, infections, or those on immunosuppressive therapy. |
It’s important to approach stem cells for type 2 diabetes with realistic expectations and an open discussion with your doctor.
Get a free online consultation
If you are interested in treating type 2 diabetes with stem cells, the next step is an online consultation. Swiss Medica offers free online consultations where our medical advisors take time to review your case, listen to your concerns, and answer all your questions.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Safety and Risks of Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
Stem cell transplant for type 2 diabetes has shown a strong safety record when performed in a regulated medical environment. At Swiss Medica, the treatment is set up to lower risks at every step, from preparing the cells to giving follow-up care.
- Cell quality and sourcing: At our hospital, stem cells are processed in certified sterile labs, tested for purity and safety, and ethically sourced. Umbilical cord–derived and adult MSCs are thoroughly screened and carry no known risk of rejection or tumor formation.
- Procedure safety: The procedure typically involves a painless IV infusion and local applications. Patients are monitored throughout, and most feel fine—only mild fatigue or a brief fever may occur in some cases.
- Post-treatment risks: Following therapy, your doctor may adjust your diabetes medication at home as insulin sensitivity improves. Our doctors monitor your progress through regular follow-ups to ensure safe, gradual changes.
Is It Safe for Older Patients?
The procedures are gentle enough that even people in their 70s or beyond tolerate them well. Before treatment, each patient’s individual health conditions must be thoroughly evaluated to ensure safety and suitability. While older adults may experience slower regenerative responses—and therefore slower improvements compared with younger patients—the overall safety profile remains high.
Stem cell therapy has been researched for decades and shown to be safe for many conditions. Learn more about the safety of mesenchymal stem cells.
Read moreSwiss Medica’s Approach to Diabetes Treatment
Swiss Medica, one of the top stem cell clinics in the world, has worked in the field of regenerative medicine for more than 14 years. Here’s what defines our approach to stem cell transplants for type 2 diabetes.
Advanced Stem Cell Processing and Laboratory Quality
- The in-house GMP-certified laboratory ensures full control from cell isolation to preparation.
- All processing, testing, and expansion are done under strict quality and safety standards.
- Each batch of stem cells is verified for potency and purity.
Individualized Treatment Protocols
- Personalized plans: Therapy is tailored to each patient’s condition, goals, and health status.
- Individualized dosage: Doctors choose the optimal cell source and dose (autologous, donor, or combined).
- Integrated rehabilitation: Support from physiotherapists and adjunct therapies enhances recovery.
- Close medical attention: A low patient-to-doctor ratio (~3–4 per doctor) ensures attentive care.
Comprehensive Patient Care
Throughout treatment with stem cells for type 2 diabetes, patients receive continuous medical and personal support. Before therapy, records and tests are reviewed carefully. During the stay, care is closely monitored, and after therapy, recovery guidance and regular follow-ups help maintain results.
We have over 14 years of experience in regenerative medicine. Learn more about our hospital, medical team, and facilities.
Read moreOur Belgrade Hospital: Why Choose Swiss Medica Beyond Diabetes Treatment
In 2024, Swiss Medica opened a 10,000 m² state-of-the-art hospital in Belgrade, now the main headquarters. It features:
- Five departments focused on regenerative, neurological, and metabolic care
- 24/7 medical supervision and advanced rehabilitation facilities
- Comfortable, home-like patient rooms
- Experienced team with 10,000+ patients treated since 2011
- Full support with airport transfers, accommodation, and ongoing follow-up care
Swiss Medica hospital is a modern facility with its own lab, private treatment rooms, comfortable accommodations, and healthy meals.
Real Patient Experience
Our patient from Ireland shares his experience after undergoing stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes:
“I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2005, and as the condition progressed, I started looking for better ways to manage it. After learning about stem cell therapy and hearing success stories from other patients, I decided to undergo treatment at Swiss Medica. The doctors provided clear guidance and explanations, which gave me full confidence in my decision.
After receiving the therapy, I noticed visible improvements—my blood sugar levels became more stable, my energy increased, and I felt overall healthier.”
This is just one of many inspirational patient stories. On our YouTube channel, you can find over 600 testimonials for various conditions.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes
When considering stem cell therapy for type 2 diabetes, cost is an important factor to consider.
The stem cell treatment cost depends on several key factors: the type and source of cells, the dosage or number of cells required, the length and complexity of the treatment program, and the location and standards of the clinic. Here is a brief review of costs in the best countries for stem cell therapy:
| Location / Provider | Typical Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes |
| United States / UK | $20,000–$50,000+ |
| Western Europe | €40,000–€60,000+ |
| Serbia | €7,000–€31,000* |
*Prices are indicative, based on January 2025, and may vary with condition severity and cell quantity required.
Even the highest treatment price at Swiss Medica is much lower than in Western countries.
Getting Started: Your Next Steps
At Swiss Medica, treatment typically involves 4 main steps.
-
1
Consultation evaluation
Start by contacting Swiss Medica for a free online consultation. You’ll discuss your medical history, current treatment, and overall health. We will review your records to determine if stem cell therapy is suitable for you.
-
2
Planning and travel
Once you decide to proceed, the clinic helps arrange travel, accommodation, and scheduling.
-
3
Treatment period
You’ll stay at the clinic for several days, depending on your plan. Stem cells are administered through an IV or targeted injections, and additional therapies may be included. The medical team monitors you closely and adjusts your medications if needed.
-
4
Follow-up
After leaving home, you’ll have regular online check-ins to monitor your progress and discuss long-term outcomes, with the option of additional treatment if necessary.
Contact us
We understand that deciding on a treatment like this is a big step. The best thing you can do is gather knowledge specific to your case. A free, no-obligation consultation can help you learn how stem cell therapy may apply to your case.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
FAQ
1. How soon can I expect results?
Most patients may notice gradual improvements within weeks, with notable results like reduced medication requirements appearing after 2–3 months and stabilizing by 6 months.
2. What benefits can I expect from stem cell therapy for diabetes, and how long will they last?
The benefits vary, but many patients experience improved blood sugar control for months to years following a single treatment. The effect can fade over time, but maintaining a healthy lifestyle helps prolong results.
3. How many treatments are needed?
Usually, one treatment course is enough, involving one or a few closely scheduled injections. Some patients with advanced diabetes may need a follow-up session months later, depending on their response.
4. Can stem cells cure type 2 diabetes?
Many patients ask, “Can stem cell therapy reverse type 2 diabetes?” Stem cells are not a cure, but they can help improve blood sugar control when combined with traditional treatments.
List of References:
Kashbour, M., Abdelmalik, A., Yassin, M.N.A. et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for type 1 & 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetol Metab Syndr 17, 189 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-025-01619-6
Wu Z, Huang S, Li S, Cai J, Huang L, Wu W, Chen J, Tan J. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell and mononuclear cell combination therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled study with 8-year follow-up. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Sep 30;15(1):339. doi.org/10.1186/s13287-024-03907-w
Bhansali A, Asokumar P, Walia R, Bhansali S, Gupta V, Jain A, Sachdeva N, Sharma RR, Marwaha N, Khandelwal N. Efficacy and safety of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(9):1075-85. doi.org/10.3727/096368913X665576
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor